Page 94 - Read Online
P. 94
Rastogi. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:47 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.35 Page 5 of 17
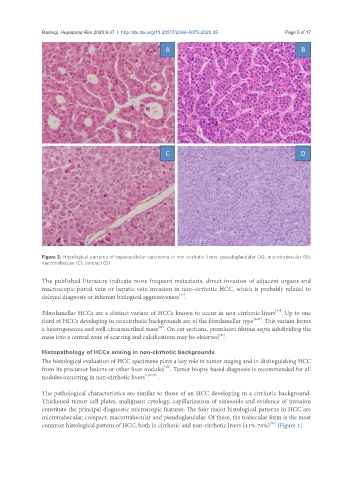
Figure 2. Histological patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic livers: pseudoglandular (A), microtrabecular (B),
macrotrabecular (C), compact (D)
The published literature indicate more frequent metastasis, direct invasion of adjacent organs and
macroscopic portal vein or hepatic vein invasion in non-cirrhotic HCC, which is probably related to
[41]
delayed diagnosis or inherent biological aggressiveness .
[44]
Fibrolamellar HCCs are a distinct variant of HCCs known to occur in non-cirrhotic livers . Up to one
third of HCCs developing in noncirrhotic backgrounds are of the fibrolamellar type [2,45] . This variant forms
[46]
a heterogeneous and well-circumscribed mass . On cut sections, prominent fibrous septa subdividing the
[47]
mass into a central zone of scarring and calcifications may be observed .
Histopathology of HCCs arising in non-cirrhotic backgrounds
The histological evaluation of HCC specimens plays a key role in tumor staging and in distinguishing HCC
[48]
from its precursor lesions or other liver nodules . Tumor biopsy based diagnosis is recommended for all
nodules occurring in non-cirrhotic livers [1,49,50] .
The pathological characteristics are similar to those of an HCC developing in a cirrhotic background.
Thickened tumor cell plates, malignant cytology, capillarization of sinusoids and evidence of invasion
constitute the principal diagnostic microscopic features. The four major histological patterns in HCC are
microtrabecular, compact, macrotrabecular and pseudoglandular. Of these, the trabecular form is the most
[51]
common histological pattern of HCC, both in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic livers (41%-76%) [Figure 2].