Page 20 - Read Online
P. 20
Tao et al. Energy Mater 2022;2:200036 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2022.46 Page 5 of 35
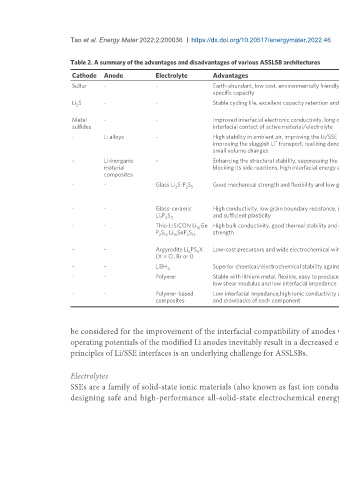
Table 2. A summary of the advantages and disadvantages of various ASSLSB architectures
Cathode Anode Electrolyte Advantages Disadvantages Ref.
Sulfur - - Earth-abundant, low cost, environmentally friendly and a high theoretical Low cathode utilization, low active loading in cathode composites, [29]
specific capacity huge volume change, low electrochemical kinetics and highly insulative
Li S - - Stable cycling life, excellent capacity retention and high discharge capacity Highly insulative and low theoretical specific capacity and matching [30]
2
with lithium-free anode materials
Metal - - Improved interfacial electronic conductivity, long cyclic life and good Low theoretical capacities, low discharge voltages and large volume [31]
sulfides interfacial contact of active material/electrolyte change
- Li alloys - High stability in ambient air, improving the Li/SSE interface contact, Increased costs, compromised overall specific capacity and higher [32]
+
improving the sluggish Li transport, realizing dendrite-free Li deposition and operating potentials
small volume changes
- Li-inorganic - Enhancing the structural stability, suppressing the lithium dendrite growth, Poor cycle life and rate capabilities, parasitic interfacial reactions and [33]
material blocking its side reactions, high interfacial energy and high bulk modulus higher operating potentials
composites
- - Glass Li S-P S Good mechanical strength and flexibility and low grain boundary resistance Low oxidation stability, sensitivity to moisture, poor compatibility with [34]
2 2 5
cathode materials, low ionic conductivities at room temperature and
narrow voltage windows
- - Glass-ceramic High conductivity, low grain boundary resistance, inherent isotropic character Hygroscopic, low oxidation stability and limited voltage windows [35]
Li P S and sufficient plasticity
7 3 11
- - Thio-LISICON Li Ge High bulk conductivity, good thermal stability and outstanding mechanical Poor stability against Li metal anodes, narrow electrochemical stability [36]
10
P S Li SnP S strength windows, high interfacial impedance and degraded physical stability
2 12 10 2 12
with electrodes
- - Argyrodite Li PS X Low-cost precursors and wide electrochemical window Unstable with polar organic solvents and low ionic conductivities at [37]
6 5
(X = Cl, Br or I) room temperature
- - LiBH Superior chemical/electrochemical stability against Li metal Low room-temperature ionic conductivity [38]
4
- - Polymer Stable with lithium metal, flexible, easy to produce a large-area membrane, Limited thermal stability, low ionic conductivities at room temperature [39]
low shear modulus and low interfacial impedance and narrow electrochemical stability windows
- - Polymer-based Low interfacial impedance,high ionic conductivity and balancing the merits Low mechanical strength and [40]
composites and drawbacks of each component poor thermal stability
be considered for the improvement of the interfacial compatibility of anodes with SSEs, as the anodes are properly designed. However, the relatively higher
operating potentials of the modified Li anodes inevitably result in a decreased energy density. An in-depth understanding of the fundamentals and engineering
principles of Li/SSE interfaces is an underlying challenge for ASSLSBs.
Electrolytes
SSEs are a family of solid-state ionic materials (also known as fast ion conductors or superionic solids) that exhibit remarkable technological potential for
designing safe and high-performance all-solid-state electrochemical energy storage systems, because of their extremely high room temperature ionic