Page 120 - Read Online
P. 120
Page 8 of 14 Liang et al. Energy Mater 2023;3:300006 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2022.63
-2
-2
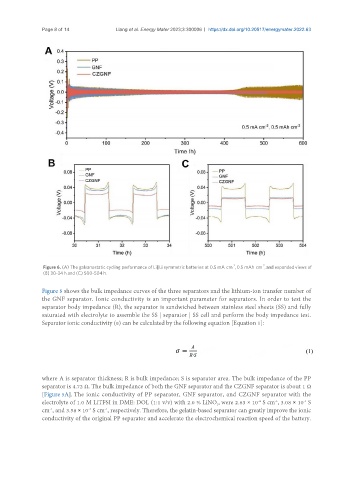
Figure 6. (A) The galvanostatic cycling performance of Li||Li symmetric batteries at 0.5 mA cm , 0.5 mAh cm , and expanded views of
(B) 30-34 h and (C) 500-504 h.
Figure 5 shows the bulk impedance curves of the three separators and the lithium-ion transfer number of
the GNF separator. Ionic conductivity is an important parameter for separators. In order to test the
separator body impedance (R), the separator is sandwiched between stainless steel sheets (SS) and fully
saturated with electrolyte to assemble the SS | separator | SS cell and perform the body impedance test.
Separator ionic conductivity (σ) can be calculated by the following equation [Equation 1]:
where A is separator thickness; R is bulk impedance; S is separator area. The bulk impedance of the PP
separator is 4.72 Ω. The bulk impedance of both the GNF separator and the CZGNF separator is about 1 Ω
[Figure 5A]. The ionic conductivity of PP separator, GNF separator, and CZGNF separator with the
-4
electrolyte of 1.0 M LiTFSI in DME: DOL (1:1 v/v) with 2.0 % LiNO , were 2.63 × 10 S cm , 3.08 × 10 S
-3
-1
3
-1
cm , and 3.58 × 10 S cm , respectively. Therefore, the gelatin-based separator can greatly improve the ionic
-1
-3
conductivity of the original PP separator and accelerate the electrochemical reaction speed of the battery.