Page 156 - Read Online
P. 156
Page 4 of 16 Kodag et al. Dis Prev Res 2023;2:12 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/dpr.2023.11
Figure 1. shows core infrastructure elements in a Smart City. (source-reimaging pune: Mission Smart City, 2016).
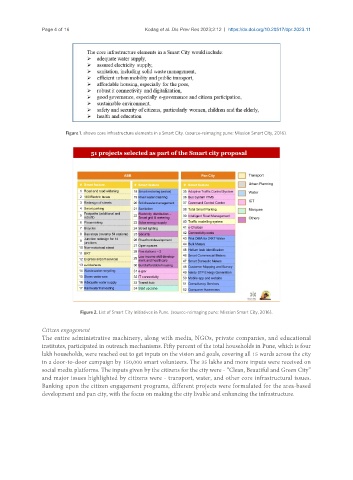
Figure 2. List of Smart City Initiatives in Pune. (source-reimaging pune: Mission Smart City, 2016).
Citizen engagement
The entire administrative machinery, along with media, NGOs, private companies, and educational
institutes, participated in outreach mechanisms. Fifty percent of the total households in Pune, which is four
lakh households, were reached out to get inputs on the vision and goals, covering all 15 wards across the city
in a door-to-door campaign by 150,000 smart volunteers. The 35 lakhs and more inputs were received on
social media platforms. The inputs given by the citizens for the city were - “Clean, Beautiful and Green City”
and major issues highlighted by citizens were - transport, water, and other core infrastructural issues.
Banking upon the citizen engagement programs, different projects were formulated for the area-based
development and pan city, with the focus on making the city livable and enhancing the infrastructure.