Page 94 - Read Online
P. 94
Gutierrez et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2021;4:414-23 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2020.113 Page 420
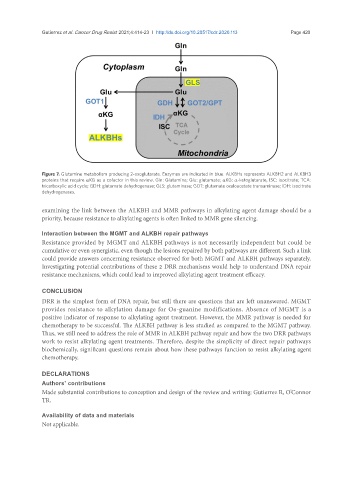
Figure 7. Glutamine metabolism producing 2-oxoglutarate. Enzymes are indicated in blue. ALKBHs represents ALKBH2 and ALKBH3
proteins that require αKG as a cofactor in this review. Gln: Glutamine; Glu: glutamate; αKG: α-ketoglutarate, ISC: isocitrate; TCA:
tricarboxylic acid cycle; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GLS: glutaminase; GOT: glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase; IDH: isocitrate
dehydrogenases.
examining the link between the ALKBH and MMR pathways in alkylating agent damage should be a
priority, because resistance to alkylating agents is often linked to MMR gene silencing.
Interaction between the MGMT and ALKBH repair pathways
Resistance provided by MGMT and ALKBH pathways is not necessarily independent but could be
cumulative or even synergistic, even though the lesions repaired by both pathways are different. Such a link
could provide answers concerning resistance observed for both MGMT and ALKBH pathways separately.
Investigating potential contributions of these 2 DRR mechanisms would help to understand DNA repair
resistance mechanisms, which could lead to improved alkylating agent treatment efficacy.
CONCLUSION
DRR is the simplest form of DNA repair, but still there are questions that are left unanswered. MGMT
provides resistance to alkylation damage for O6-guanine modifications. Absence of MGMT is a
positive indicator of response to alkylating agent treatment. However, the MMR pathway is needed for
chemotherapy to be successful. The ALKBH pathway is less studied as compared to the MGMT pathway.
Thus, we still need to address the role of MMR in ALKBH pathway repair and how the two DRR pathways
work to resist alkylating agent treatments. Therefore, despite the simplicity of direct repair pathways
biochemically, significant questions remain about how these pathways function to resist alkylating agent
chemotherapy.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Made substantial contributions to conception and design of the review and writing: Gutierrez R, O’Connor
TR.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.