Page 90 - Read Online
P. 90
Gutierrez et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2021;4:414-23 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2020.113 Page 416
Figure 2. General DNA repair pathways implicated in the elimination of DNA damage from alkylating agents. The blue sections
6
and dotted lines have not yet been described in the literature. The possible base pairs for O meG, 1-meA, and 3-meC are indicated.
If cells complete the first round of replication, following a second round of replication, a mutation is fixed in 50% of the cells. If
[3]
replication is arrested and a second round of replication occurs, a DSB can form. Modeled after Reference . BER: Base excision repair;
NER: nucleotide excision repair; MMR: mismatch repair; DSB: double-strand break; HDR: homology-directed repair; NHEJ: non-
6
homologous end-joining; SSB: single strand break; ATR: ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related; ATRIP: ATR interacting protein; O meG:
6
O methylguanine; 1-meA: 1-methyladenine; 3-meC: 3-methylcytosine.
6
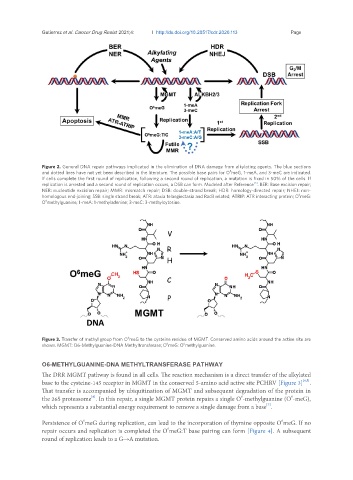
Figure 3. Transfer of methyl group from O meG to the cysteine residue of MGMT. Conserved amino acids around the active site are
6
6
shown. MGMT: O6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase; O meG: O methylguanine.
O6-METHYLGUANINE-DNA METHYLTRANSFERASE PATHWAY
The DRR MGMT pathway is found in all cells. The reaction mechanism is a direct transfer of the alkylated
[4,5]
base to the cysteine-145 receptor in MGMT in the conserved 5-amino acid active site PCHRV [Figure 3] .
That transfer is accompanied by ubiquitination of MGMT and subsequent degradation of the protein in
6
6
[6]
the 26S proteasome . In this repair, a single MGMT protein repairs a single O -methylguanine (O -meG),
[7]
which represents a substantial energy requirement to remove a single damage from a base .
6
6
Persistence of O meG during replication, can lead to the incorporation of thymine opposite O meG. If no
6
repair occurs and replication is completed the O meG:T base pairing can form [Figure 4]. A subsequent
round of replication leads to a G→A mutation.