Page 200 - Read Online
P. 200
Page 696 Alonso-Peña et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:680-709 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.006
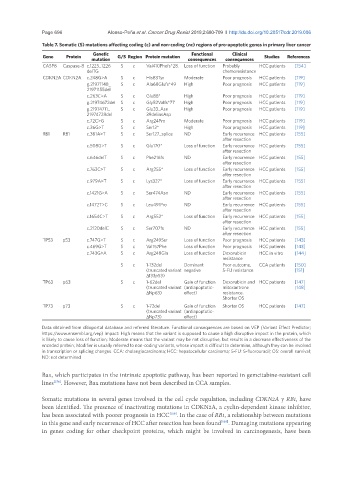
Table 7. Somatic (S) mutations affecting coding (c) and non-coding (nc) regions of pro-apoptotic genes in primary liver cancer
Gene Protein Genetic G/S Region Protein mutation Functional Clinical Studies References
mutation consequences consequences
CASP8 Caspase-8 c.1225_1226 S c Val410Phefs*28. Loss of function Probably HCC patients [154]
delTG chemoresistance
CDKN2A CDKN2A c.248G>A S c His83Tyr Moderate Poor prognosis HCC patients [119]
g.21971148_ S c Ala68Glufs*49 High Poor prognosis HCC patients [119]
21971155del
c.263C>A S c Glu88* High Poor prognosis HCC patients [119]
g.21974672del S c Gly52Valfs*77 High Poor prognosis HCC patients [119]
g.21974711_ S c Glu33_Asn High Poor prognosis HCC patients [119]
21974728del 39delinsAsp
c.72C>G S c Arg24Pro Moderate Poor prognosis HCC patients [119]
c.36G>T S c Ser12* High Poor prognosis HCC patients [119]
RB1 RB1 c.381A>T S c Ser127_splice ND Early recurrence HCC patients [155]
after resection
c.508G>T S c Glu170* Loss of function Early recurrence HCC patients [155]
after resection
c.646delT S c Phe216fs ND Early recurrence HCC patients [155]
after resection
c.763C>T S c Arg255* Loss of function Early recurrence HCC patients [155]
after resection
c.979A>T S c Lys327* Loss of function Early recurrence HCC patients [155]
after resection
c.1421G>A S c Ser474Asn ND Early recurrence HCC patients [155]
after resection
c.1472T>C S c Leu491Pro ND Early recurrence HCC patients [155]
after resection
c.1654C>T S c Arg552* Loss of function Early recurrence HCC patients [155]
after resection
c.2120delC S c Ser707fs ND Early recurrence HCC patients [155]
after resection
TP53 p53 c.747G>T S c Arg249Ser Loss of function Poor prognosis HCC patients [143]
c.469G>T S c Val157Phe Loss of function Poor prognosis HCC patients [143]
c.743G>A S c Arg248Gln Loss of function Doxorubicin HCC in vitro [144]
resistance
S c 1-132del Dominant Poor outcome, CCA patients [150]
(truncated variant negative 5-FU resistance [151]
Δ133p53)
TP63 p63 S c 1-62del Gain of function Doxorubicin and HCC patients [147]
(truncated variant (antiapoptotic- mitoxantrone [148]
ΔNp63) effect) resistance.
Shorter OS
TP73 p73 S c 1-72del Gain of function Shorter OS HCC patients [147]
(truncated variant (antiapoptotic-
ΔNp73) effect)
Data obtained from cBioportal database and referred literature. Functional consequences are based on VEP (Variant Effect Predictor;
https://www.ensembl.org/vep) impact: High means that the variant is supposed to cause a high disruptive impact in the protein, which
is likely to cause loss of function; Moderate means that the variant may be not disruptive, but results in a decrease effectiveness of the
encoded protein; Modifier is usually referred to non-coding variants, whose impact is difficult to determine, although they can be involved
in transcription or splicing changes. CCA: cholangiocarcinoma; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; OS: overall survival;
ND: not determined
Bax, which participates in the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, has been reported in gemcitabine-resistant cell
lines . However, Bax mutations have not been described in CCA samples.
[156]
Somatic mutations in several genes involved in the cell cycle regulation, including CDKN2A y RB1, have
been identified. The presence of inactivating mutations in CDKN2A, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor,
has been associated with poorer prognosis in HCC . In the case of RB1, a relationship between mutations
[119]
in this gene and early recurrence of HCC after resection has been found . Damaging mutations appearing
[155]
in genes coding for other checkpoint proteins, which might be involved in carcinogenesis, have been