Page 205 - Read Online
P. 205
Alonso-Peña et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:680-709 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.006 Page 701
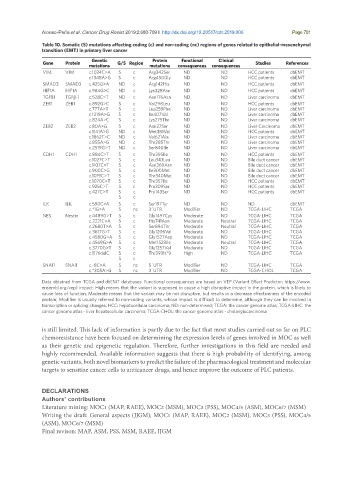
Table 10. Somatic (S) mutations affecting coding (c) and non-coding (nc) regions of genes related to epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) in primary liver cancer
Genetic Protein Functional Clinical
Gene Protein G/S Region Studies References
mutations mutations consequences consequences
VIM VIM c.1024C>A S c Arg342Ser ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
c.1348A>G S c Arg450Gly ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
SMAD3 SMAD3 c.425G>A ND c Arg142His ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
HIF1A HIF1A c.984G>C ND c Lys328Asn ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
TGFB1 TGFβ-1 c.528C>T ND c Asn176Asn ND ND Liver carcinoma dbEMT
ZEB1 ZEB1 c.892G>C S c Val298Leu ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
c.777A>T S c Leu259Phe ND ND Liver carcinoma dbEMT
c.1219A>G S c Ile407Val ND ND Liver carcinoma dbEMT
c.824A>C S c Lys275Thr ND ND Liver carcinoma dbEMT
ZEB2 ZEB2 c.80A>G S c Asn27Ser ND ND Liver Carcinoma dbEMT
c.1141A>G ND c Met381Val ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
c.1862T>C ND c Val621Ala ND ND Liver carcinoma dbEMT
c.855A>G ND c Thr285Thr ND ND Liver carcinoma dbEMT
c.2519G>T ND c Ser840Ile ND ND Liver carcinoma dbEMT
CDH1 CDH1 c.884C>T S c Thr295Ile ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
c.1027C>T S c Leu343Leu ND ND Bile duct cancer dbEMT
c.1107C>T S c Asn369Asn ND ND Bile duct cancer dbEMT
c.900C>G S c Ile300Met ND ND Bile duct cancer dbEMT
c.1019C>T S c Thr340Met ND ND Bile duct cancer dbEMT
c.1070C>T S c Thr357Ile ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
c.925C>T S c Pro309Ser ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
c.427C>T S c Pro143Ser ND ND HCC patients dbEMT
S c
ILK ILK c.590C>A S c Ser197Tyr ND ND ND dbEMT
c.*1G>A S nc 3´UTR Modifier ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
NES Nestin c.4489G>T S c Gly1497Cys Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.2221C>A S c His741Asn Moderate Neutral TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.2680T>A S c Ser894Thr Moderate Neutral TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.3617G>T S c Gly1206Val Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.4580G>A S c Gly1527Asp Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.4569G>A S c Met1523Ile Moderate Neutral TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.3770G>T S c Gly1257Val Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.1176delC S c Thr393fs*9 High ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
S c
SNAI1 SNAI1 c.-8C>A S nc 5´UTR Modifier ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.*305A>G S nc 3´UTR Modifier ND TCGA-CHOL TCGA
Data obtained from TCGA and dbEMT databases. Functional consequences are based on VEP (Variant Effect Predictor; https://www.
ensembl.org/vep) impact: High means that the variant is supposed to cause a high disruptive impact in the protein, which is likely to
cause loss of function; Moderate means that the variant may be not disruptive, but results in a decrease effectiveness of the encoded
protein; Modifier is usually referred to non-coding variants, whose impact is difficult to determine, although they can be involved in
transcription or splicing changes. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; ND: non-determined; TCGA: the cancer genome atlas; TCGA-LIHC: the
cancer genome atlas - liver hepatocellular carcinoma; TCGA-CHOL: the cancer genome atlas - cholangiocarcinoma
is still limited. This lack of information is partly due to the fact that most studies carried out so far on PLC
chemoresistance have been focused on determining the expression levels of genes involved in MOC as well
as their genetic and epigenetic regulation. Therefore, further investigations in this field are needed and
highly recommended. Available information suggests that there is high probability of identifying, among
genetic variants, both novel biomarkers to predict the failure of the pharmacological treatment and molecular
targets to sensitize cancer cells to anticancer drugs, and hence improve the outcome of PLC patients.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Literature mining: MOC1 (MAP, RAEE), MOC2 (MSM), MOC3 (PSS), MOC4/5 (ASM), MOC6/7 (MSM)
Writing the draft: General aspects (JJGM); MOC1 (MAP, RAEE), MOC2 (MSM), MOC3 (PSS), MOC4/5
(ASM), MOC6/7 (MSM)
Final revison: MAP, ASM, PSS, MSM, RAEE, JJGM