Page 198 - Read Online
P. 198
Page 694 Alonso-Peña et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:680-709 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.006
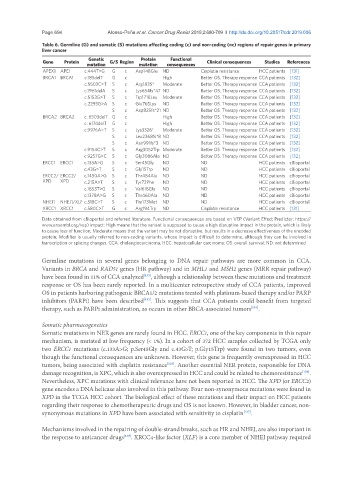
Table 6. Germline (G) and somatic (S) mutations affecting coding (c) and non-coding (nc) regions of repair genes in primary
liver cancer
Genetic Protein Functional
Gene Protein G/S Region Clinical consequences Studies References
mutation mutation consequences
APEX1 APE1 c.444T>G G c Asp148Glu ND Cisplatin resistance HCC patients [131]
BRCA1 BRCA1 c.185delT G c High Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
c.5503C>T S c Arg1835* Moderate Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
c.1961delA S c Lys654fs*47 ND Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
c.5153G>T S c Trp1718Leu Moderate Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
c.2293G>A S c Glu765Lys ND Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
S c Asp825fs*21 ND Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
BRCA2 BRCA2 c. 6503delT G c High Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
c. 6174delT G c High Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
c.9976A>T S c Lys3326* Moderate Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
S c Leu2368fs*8 ND Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
S c Asn991fs*3 ND Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
c.9154C>T S c Arg3052Trp Moderate Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
c.9257G>C S c Gly3086Ala ND Better OS. Therapy response CCA patients [132]
ERCC1 ERCC1 c.133A>G S c Ser45Gly ND ND HCC patients cBioportal
c.43G>T S c Gly15Trp ND ND HCC patients cBioportal
ERCC2/ ERCC2/ c.1450A>G S c Thr484Ala ND ND HCC patients cBioportal
XPD XPD c.215A>T S c Tyr72Phe ND ND HCC patients cBioportal
c.1853T>G S c Val618Gly ND ND HCC patients cBioportal
c.1378A>G S c Thr460Ala ND ND HCC patients cBioportal
NHEJ1 NHEJ1/XLF c.518C>T S c Thr173Met ND ND HCC patients cBioportal
XRCC1 XRCC1 c.580C>T G c Arg194Trp ND Cisplatin resistance HCC patients [131]
Data obtained from cBioportal and referred literature. Functional consequences are based on VEP (Variant Effect Predictor; https://
www.ensembl.org/vep) impact: High means that the variant is supposed to cause a high disruptive impact in the protein, which is likely
to cause loss of function; Moderate means that the variant may be not disruptive, but results in a decrease effectiveness of the encoded
protein; Modifier is usually referred to non-coding variants, whose impact is difficult to determine, although they can be involved in
transcription or splicing changes. CCA: cholangiocarcinoma; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; OS: overall survival; ND: not determined
Germline mutations in several genes belonging to DNA repair pathways are more common in CCA.
Variants in BRCA and RAD51 genes (HR pathway) and in MHL1 and MSH2 genes (MRR repair pathway)
have been found in 11% of CCA analyzed , although a relationship between these mutations and treatment
[133]
response or OS has been rarely reported. In a multicenter retrospective study of CCA patients, improved
OS in patients harboring pathogenic BRCA1/2 mutations treated with platinum-based therapy and/or PARP
inhibitors (PARPi) have been described . This suggests that CCA patients could benefit from targeted
[132]
therapy, such as PARPi administration, as occurs in other BRCA-associated tumors .
[134]
Somatic pharmacogenetics
Somatic mutations in NER genes are rarely found in HCC. ERCC1, one of the key components in this repair
mechanism, is mutated at low frequency (< 1%). In a cohort of 372 HCC samples collected by TCGA only
two ERCC1 mutations (c.133A>G; p.Ser45Gly and c.43G>T; p.Gly15Trp) were found in two tumors, even
though the functional consequences are unknown. However, this gene is frequently overexpressed in HCC
tumors, being associated with cisplatin resistance . Another essential NER protein, responsible for DNA
[135]
damage recognition, is XPC, which is also overexpressed in HCC and could be related to chemoresistance .
[136]
Nevertheless, XPC mutations with clinical relevance have not been reported in HCC. The XPD (or ERCC2)
gene encodes a DNA helicase also involved in this pathway. Four non-synonymous mutations were found in
XPD in the TCGA HCC cohort. The biological effect of these mutations and their impact on HCC patients
regarding their response to chemotherapeutic drugs and OS is not known. However, in bladder cancer, non-
synonymous mutations in XPD have been associated with sensitivity to cisplatin .
[137]
Mechanisms involved in the repairing of double-strand breaks, such as HR and NHEJ, are also important in
the response to anticancer drugs . XRCC4-like factor (XLF) is a core member of NHEJ pathway required
[138]