Page 103 - Read Online
P. 103
Remley et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2023;6:748-67 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2023.63 Page 758
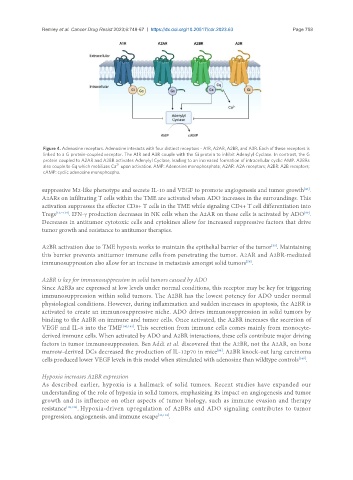
Figure 4. Adenosine receptors. Adenosine interacts with four distinct receptors - A1R, A2AR, A2BR, and A3R. Each of these receptors is
linked to a G protein-coupled receptor. The A1R and A3R couple with the Gi protein to inhibit Adenylyl Cyclase. In contrast, the G
protein coupled to A2AR and A2BR activates Adenylyl Cyclase, leading to an increased formation of intracellular cyclic AMP. A2BRs
2+
also couple to Gq which mobilizes Ca upon activation. AMP: Adenosine monophosphate; A2AR: A2A receptors; A2BR: A2B receptors;
cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophospha.
suppressive M2-like phenotype and secrete IL-10 and VEGF to promote angiogenesis and tumor growth .
[43]
A2ARs on infiltrating T cells within the TME are activated when ADO increases in the surroundings. This
activation suppresses the effector CD8+ T cells in the TME while signaling CD4+ T cell differentiation into
Tregs [137-139] . IFN-γ production decreases in NK cells when the A2AR on these cells is activated by ADO .
[99]
Decreases in antitumor cytotoxic cells and cytokines allow for increased suppressive factors that drive
tumor growth and resistance to antitumor therapies.
A2BR activation due to TME hypoxia works to maintain the epithelial barrier of the tumor . Maintaining
[39]
this barrier prevents antitumor immune cells from penetrating the tumor. A2AR and A2BR-mediated
immunosuppression also allow for an increase in metastasis amongst solid tumors .
[58]
A2BR is key for immunosuppression in solid tumors caused by ADO
Since A2BRs are expressed at low levels under normal conditions, this receptor may be key for triggering
immunosuppression within solid tumors. The A2BR has the lowest potency for ADO under normal
physiological conditions. However, during inflammation and sudden increases in apoptosis, the A2BR is
activated to create an immunosuppressive niche. ADO drives immunosuppression in solid tumors by
binding to the A2BR on immune and tumor cells. Once activated, the A2BR increases the secretion of
VEGF and IL-8 into the TME [140,141] . This secretion from immune cells comes mainly from monocyte-
derived immune cells. When activated by ADO and A2BR interactions, these cells contribute major driving
factors in tumor immunosuppression. Ben Addi et al. discovered that the A2BR, not the A2AR, on bone
marrow-derived DCs decreased the production of IL-12p70 in mice . A2BR knock-out lung carcinoma
[84]
cells produced lower VEGF levels in this model when stimulated with adenosine than wildtype controls .
[140]
Hypoxia increases A2BR expression
As described earlier, hypoxia is a hallmark of solid tumors. Recent studies have expanded our
understanding of the role of hypoxia in solid tumors, emphasizing its impact on angiogenesis and tumor
growth and its influence on other aspects of tumor biology, such as immune evasion and therapy
resistance [18,142] . Hypoxia-driven upregulation of A2BRs and ADO signaling contributes to tumor
progression, angiogenesis, and immune escape [44,113] .