Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
Page 272 Yoseph et al. Art Int Surg 2024;4:267-77 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.38
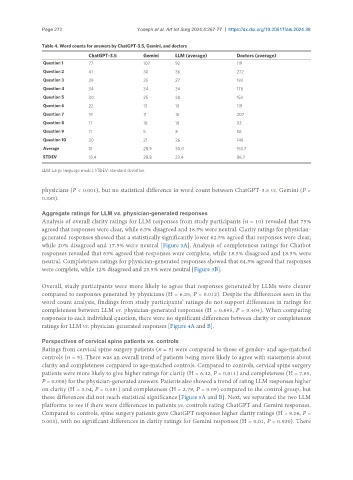
Table 4. Word counts for answers by ChatGPT-3.5, Gemini, and doctors
ChatGPT-3.5 Gemini LLM (average) Doctors (average)
Question 1 77 107 92 119
Question 2 41 30 36 272
Question 3 29 25 27 193
Question 4 34 34 34 178
Question 5 30 25 28 153
Question 6 22 13 18 119
Question 7 19 11 15 207
Question 8 17 18 18 93
Question 9 11 5 8 56
Question 10 30 21 26 149
Average 31 28.9 30.0 153.7
STDEV 18.4 28.8 23.4 86.7
LLM: Large language model; STDEV: standard deviation.
physicians (P < 0.001), but no statistical difference in word count between ChatGPT-3.5 vs. Gemini (P =
0.383).
Aggregate ratings for LLM vs. physician-generated responses
Analysis of overall clarity ratings for LLM responses from study participants (n = 10) revealed that 75%
agreed that responses were clear, while 6.5% disagreed and 18.5% were neutral. Clarity ratings for physician-
generated responses showed that a statistically significantly lower 62.5% agreed that responses were clear,
while 20% disagreed and 17.5% were neutral [Figure 3A]. Analysis of completeness ratings for Chatbot
responses revealed that 63% agreed that responses were complete, while 18.5% disagreed and 18.5% were
neutral. Completeness ratings for physician-generated responses showed that 64.5% agreed that responses
were complete, while 12% disagreed and 23.5% were neutral [Figure 3B].
Overall, study participants were more likely to agree that responses generated by LLMs were clearer
compared to responses generated by physicians (H = 6.25, P = 0.012). Despite the differences seen in the
word count analysis, findings from study participants’ ratings do not support differences in ratings for
completeness between LLM vs. physician-generated responses (H = 0.695, P = 0.404). When comparing
responses to each individual question, there were no significant differences between clarity or completeness
ratings for LLM vs. physician-generated responses [Figure 4A and B].
Perspectives of cervical spine patients vs. controls
Ratings from cervical spine surgery patients (n = 5) were compared to those of gender- and age-matched
controls (n = 5). There was an overall trend of patients being more likely to agree with statements about
clarity and completeness compared to age-matched controls. Compared to controls, cervical spine surgery
patients were more likely to give higher ratings for clarity (H = 6.42, P = 0.011) and completeness (H = 7.65,
P = 0.006) for the physician-generated answers. Patients also showed a trend of rating LLM responses higher
on clarity (H = 3.04, P = 0.081) and completeness (H = 2.79, P = 0.09) compared to the control group, but
these differences did not reach statistical significance [Figure 5A and B]. Next, we separated the two LLM
platforms to see if there were differences in patients vs. controls rating ChatGPT and Gemini responses.
Compared to controls, spine surgery patients gave ChatGPT responses higher clarity ratings (H = 9.06, P =
0.003), with no significant differences in clarity ratings for Gemini responses (H = 0.01, P = 0.930). There