Page 68 - Read Online
P. 68
Kimbowa et al. Art Int Surg 2024;4:149-69 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.20 Page 161
[66]
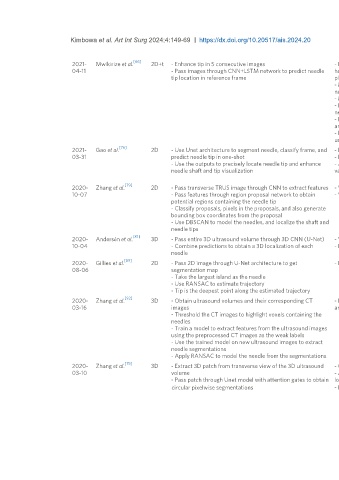
2021- Mwikirize et al. 2D+t - Enhance tip in 5 consecutive images - Does not rely on needle shaft visibility, - Straight needles
04-11 - Pass images through CNN+LSTM network to predict needle hence, works for both in plane and out of - Does not localize the shaft- Limited evaluations performed
tip location in reference frame plane detection for needle sizes, motion and high intensity artifacts, insertion
- Models temporal dynamics associated with angles, tissue types, domain invariance across imaging
needle tip motion systems
- More accurate
- Does not require a priori information about
needle trajectory
- Performs well in presence of high intensity
artifacts
- Not sensitive to type and size of needle
used
[76]
2021- Gao et al. 2D - Use Unet architecture to segment needle, classify frame, and - Real-time - Requires beam steering
03-31 predict needle tip in one-shot - Localization and segmentation in one shot - Needle after beam steering is visible enough (questions
- Use the outputs to precisely locate needle tip and enhance - Approach extensively evaluated using need for algorithm)
needle shaft and tip visualization various metircs - Has a classification network that is not necessary
- Can only work for in-plane needles
[79]
2020- Zhang et al. 2D - Pass transverse TRUS image through CNN to extract features - Works for multiple needles - Inference time evaluated on GPU which may not reflect
10-07 - Pass features through region proposal network to obtain - Works for 3D and 2D needle localization performance on low-compute devices
potential regions containing the needle tip - Only in-plane needle insertion
- Classify proposals, pixels in the proposals, and also generate
bounding box coordinates from the proposal
- Use DBSCAN to model the needles, and localize the shaft and
needle tips
[81]
2020- Andersén et al. 3D - Pass entire 3D ultrasound volume through 3D CNN (U-Net) - Works for multiple needles - Does not localize the needle tip
10-04 - Combine predictions to obtain a 3D localization of each - Doesn’t require any preprocessing - Only applicable to multiple needles and 3D ultrasound
needle
[89]
2020- Gillies et al. 2D - Pass 2D image through U-Net architecture to get - Evaluated on various target organs - Localization requires knowledge of needle entry direction
08-06 segmentation map - Not optimized for real-time performance
- Take the largest island as the needle
- Use RANSAC to estimate trajectory
- Tip is the deepest point along the estimated trajectory
[92]
2020- Zhang et al. 3D - Obtain ultrasound volumes and their corresponding CT - Doesn’t need manual labels as CT images - Requires CT image to train
03-16 images are used as weak labels - Limited to brachytherapy application
- Threshold the CT images to highlight voxels containing the
needles
- Train a model to extract features from the ultrasound images
using the preprocessed CT images as the weak labels
- Use the trained model on new ultrasound images to extract
needle segmentations
- Apply RANSAC to model the needle from the segmentations
[75]
2020- Zhang et al. 3D - Extract 3D patch from transverse view of the 3D ultrasound - Can detect multiple needles at once - Can only work for 3D ultrasound
03-10 volume - Achieves both segmentation and
- Pass patch through Unet model with attention gates to obtain localization of the needles simultaneously
circular pixelwise segmentations - Fast as compared to manual segmentation