Page 67 - Read Online
P. 67
Page 160 Kimbowa et al. Art Int Surg 2024;4:149-69 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.20
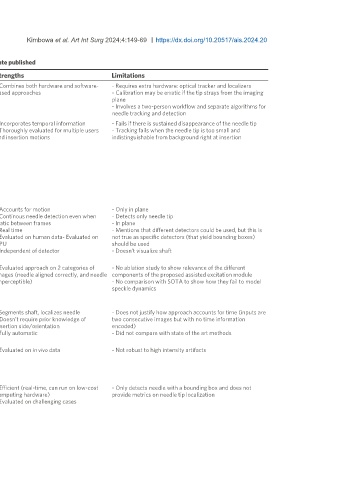
Table 2. A summary of the deep reviewed learning-based methods listed in descending order of date published
Date Author Mode Approach Strengths Limitations
[87]
2024- Che et al. 2D - Calibrate ultrasound probe and needle to optical tracker - Combines both hardware and software- - Requires extra hardware: optical tracker and localizers
01-12 - Capture needle tip using tracker based approaches - Calibration may be erratic if the tip strays from the imaging
- Represent tip in the ultrasound image coordinate system plane
- Involves a two-person workflow and separate algorithms for
needle tracking and detection
[91]
2023- Yan et al. 2D+t Consists of 3 modules - Incorporates temporal information - Fails if there is sustained disappearance of the needle tip
05-17 (1) Visual tracking module - Thoroughly evaluated for multiple users - Tracking fails when the needle tip is too small and
- Pass sampled patches from consecutive frames through the 2- and insertion motions indistinguishable from background right at insertion
branch Siamese network
- One branch dynamically extracts features from template
patches and the other extracts features from current patch
(2) Motion prediction module
- Needle velocity is estimated using displacement of the tip
between consecutive frames
(3) Data fusion
- Use MLP to independently fuse data from visual tracking
module and motion prediction module
[84]
2023- Wang et al. 2D+t (1) Enhanced ultrasound image by subtracting current frame - Accounts for motion - Only in plane
05-09 from previous frame and fusing the difference with the current - Continous needle detection even when - Detects only needle tip
frame static between frames - In plane
(2) Extract spatial constraint (bounding box around shaft) if - Real time - Mentions that different detectors could be used, but this is
present - Evaluated on human data- Evaluated on not true as specific detectors (that yield bounding boxes)
(3) Extract temporal constraint (bounding box around tip) if CPU should be used
present - Independent of detector - Doesn’t visualize shaft
(4) Combine the constraints to localize needle tip
[88]
2023- Zade et al. 2D+t - Extract motion field’s amplitude and phase from successive - Evaluated approach on 2 categories of - No ablation study to show relevance of the different
02-06 frames images (needle aligned correctly, and needle components of the proposed assisted excitation module
- Extract spatiotemporal features from the motion fields imperceptible) - No comparison with SOTA to show how they fail to model
- Pass features through detector that outputs a vector of size speckle dynamics
values including pixelwise line parameters (tx,ty,theta), and
probabilities for needle shaft and tip
[78]
2021- Chen et al. 2D - 2 frameworks - Segments shaft, localizes needle - Does not justify how approach accounts for time (inputs are
10-22 (1) Predict segmentation from two adjacent images - Doesn’t require prior knowledge of two consecutive images but with no time information
(2) 2 models - one segments shaft, the other segments needle insertion side/orientation encoded)
tip from ROIs extracted from the predictions of (1) - Fully automatic - Did not compare with state of the art methods
- Use segmentations to find
[77]
2021- Wijata et al. 2D - Pass image through Unet like architecture - Evaluated on in vivo data - Not robust to high intensity artifacts
06-28 - Architecture uses large kernels (11 × 11, 9 × 9, 7 × 7) to detect
large objects
- Apply Radon transform to determine needle trajectory
- back-transform trajectory back to binary image
[85]
2021- Rubin et al. 3D - Pass k previous frames to 3D CNN (including current frame) - Efficient (real-time, can run on low-cost - Only detects needle with a bounding box and does not
05-11 - Repeatedly apply 3D convolution to obtain a single feature computing hardware) provide metrics on needle tip localization
map for temporal information - Evaluated on challenging cases
- Pass the feature map through a 2D detector
- 2D detector outputs bounding box of needle in current frame