Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
Tovar et al. Art Int Surg 2023;3:14-26 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2022.38 Page 16
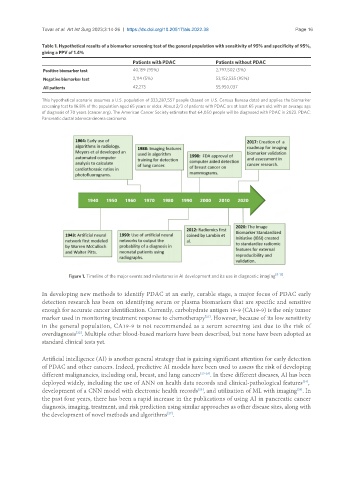
Table 1. Hypothetical results of a biomarker screening test of the general population with sensitivity of 95% and specificity of 95%,
giving a PPV of 1.4%
Patients with PDAC Patients without PDAC
Positive biomarker test 40,159 (95%) 2,797,502 (5%)
Negative biomarker test 2,114 (5%) 53,152,535 (95%)
All patients 42,273 55,950,037
This hypothetical scenario assumes a U.S. population of 333,287,557 people (based on U.S. Census Bureau data) and applies the biomarker
screening test to 16.8% of the population aged 65 years or older. About 2/3 of patients with PDAC are at least 65 years old, with an average age
of diagnosis of 70 years (cancer.org). The American Cancer Society estimates that 64,050 people will be diagnosed with PDAC in 2023. PDAC:
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma carcinoma.
[6-13]
Figure 1. Timeline of the major events and milestones in AI development and its use in diagnostic imaging .
In developing new methods to identify PDAC at an early, curable stage, a major focus of PDAC early
detection research has been on identifying serum or plasma biomarkers that are specific and sensitive
enough for accurate cancer identification. Currently, carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) is the only tumor
[21]
marker used in monitoring treatment response to chemotherapy . However, because of its low sensitivity
in the general population, CA19-9 is not recommended as a serum screening test due to the risk of
overdiagnosis . Multiple other blood-based markers have been described, but none have been adopted as
[22]
standard clinical tests yet.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another general strategy that is gaining significant attention for early detection
of PDAC and other cancers. Indeed, predictive AI models have been used to assess the risk of developing
different malignancies, including oral, breast, and lung cancers [23-26] . In these different diseases, AI has been
[24]
deployed widely, including the use of ANN on health data records and clinical-pathological features ,
development of a CNN model with electronic health records , and utilization of ML with imaging . In
[26]
[25]
the past four years, there has been a rapid increase in the publications of using AI in pancreatic cancer
diagnosis, imaging, treatment, and risk prediction using similar approaches as other disease sites, along with
the development of novel methods and algorithms .
[27]