Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Bektaş et al. Art Int Surg 2022;2:132-43 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2022.20 Page 136
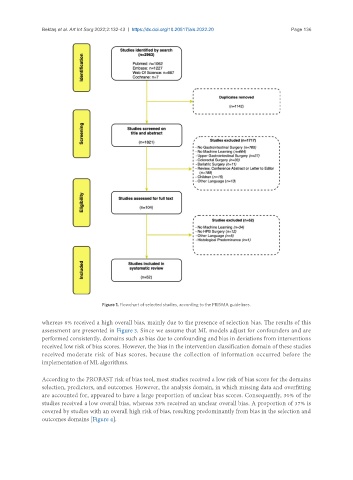
Figure 1. Flowchart of selected studies, according to the PRISMA guidelines.
whereas 8% received a high overall bias, mainly due to the presence of selection bias. The results of this
assessment are presented in Figure 3. Since we assume that ML models adjust for confounders and are
performed consistently, domains such as bias due to confounding and bias in deviations from interventions
received low risk of bias scores. However, the bias in the intervention classification domain of these studies
received moderate risk of bias scores, because the collection of information occurred before the
implementation of ML algorithms.
According to the PROBAST risk of bias tool, most studies received a low risk of bias score for the domains
selection, predictors, and outcomes. However, the analysis domain, in which missing data and overfitting
are accounted for, appeared to have a large proportion of unclear bias scores. Consequently, 30% of the
studies received a low overall bias, whereas 33% received an unclear overall bias. A proportion of 37% is
covered by studies with an overall high risk of bias, resulting predominantly from bias in the selection and
outcomes domains [Figure 4].