Page 313 - Read Online
P. 313
Cervantes-Gracia et al. Vessel Plus 2020;4:27 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2020.22 Page 11 of 19
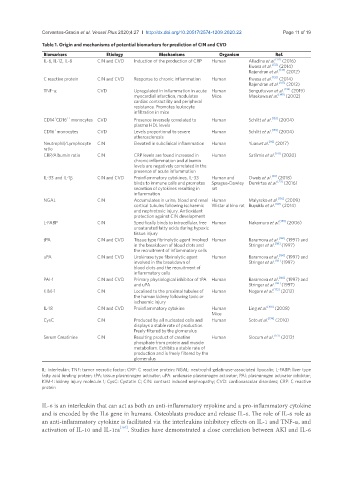
Table 1. Origin and mechanisms of potential biomarkers for prediction of CIN and CVD
Biomarkers Etiology Mechanisms Organism Ref.
IL-6, IL-12, IL-8 CIN and CVD Induction of the production of CRP Human Alladina et al. [171] (2016)
Kwasa et al. [132] (2014)
Rajendran et al. [147] (2012)
C reactive protein CIN and CVD Response to chronic inflammation Human Kwasa et al. [132] (2014)
Rajendran et al. [147] (2012)
TNF-a CVD Upregulated in inflammation in acute Human Senguttuvan et al. [148] (2019)
myocardial infarction, modulates Mice Maekawa et al. [149] (2002)
cardiac contractility and peripheral
resistance. Promotes leukocyte
infiltration in mice
++
+
CD14 CD16 monocytes CVD Presence inversely correlated to Human Schlitt et al. [153] (2004)
plasma HDL levels
+
CD16 monocytes CVD Levels proportional to severe Human Schlitt et al. [153] (2004)
atherosclerosis
Neutrophil/Lymphocyte CIN Elevated in subclinical inflammation Human Yuan et al. [92] (2017)
ratio
CRP/Albumin ratio CIN CRP levels are found increased in Human Satilmis et al. [141] (2020)
chronic inflammation and albumin
levels are negatively correlated in the
presence of acute inflammation
IL-33 and IL-1β CIN and CVD Proinflammatory cytokines, IL-33 Human and Oweis et al. [30] (2018)
binds to immune cells and promotes Sprague-Dawley Demirtas et al. [29] (2016)
secretion of cytokines resulting in rat
inflammation
NGAL CIN Accumulates in urine, blood and renal Human Malyszko et al. [156] (2009)
cortical tubules following ischaemic Wistar albino rat Buyuklu et al. [143] (2014)
and nephrotoxic injury. Antioxidant
protection against CIN development
L-FABP CIN Specifically binds to intracellular, free Human Nakamura et al. [159] (2006)
unsaturated fatty acids during hypoxic
tissue injury
tPA CIN and CVD Tissue type fibrinolytic agent involved Human Baramova et al. [160] (1997) and
in the breakdown of blood clots and Stringer et al. [161] (1997)
the recruitment of inflammatory cells
uPA CIN and CVD Urokinase type fibrinolytic agent Human Baramova et al. [160] (1997) and
involved in the breakdown of Stringer et al. [161] (1997)
blood clots and the recruitment of
inflammatory cells
PAI-1 CIN and CVD Primary physiological inhibitor of tPA Human Baramova et al. [160] (1997) and
and uPA Stringer et al. [161] (1997)
KIM-1 CIN Localised to the proximal tubules of Human Nogare et al. [172] (2012)
the human kidney following toxic or
ischaemic injury
IL-18 CIN and CVD Proinflammatory cytokine Human Ling et al. [168] (2008)
Mice
CysC CIN Produced by all nucleated cells and Human Soto et al. [174] (2010)
displays a stable rate of production.
Freely filtered by the glomerulus
Serum Creatinine CIN Resulting product of creatine Human Slocum et al. [173] (2012)
phosphate from protein and muscle
metabolism. Exhibits a stable rate of
production and is freely filtered by the
glomerulus
IL: interleukin; TNF: tumor necrotic factor; CRP: C reactive protein; NGAL: neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; L-FABP: liver type
fatty acid binding protein; tPA: tissue plasminogen activator; uPA: urokinase plasminogen activator; PAI: plasminogen activator inhibitor;
KIM-1: kidney injury molecule 1; CysC: Cystatin C; CIN: contrast induced nephropathy; CVD: cardiovascular disorders; CRP: C reactive
protein
IL-6 is an interleukin that can act as both an anti-inflammatory myokine and a pro-inflammatory cytokine
and is encoded by the IL6 gene in humans. Osteoblasts produce and release IL-6. The role of IL-6 role as
an anti-inflammatory cytokine is facilitated via the interleukins inhibitory effects on IL-1 and TNF-a, and
activation of IL-10 and IL-1ra [167] . Studies have demonstrated a close correlation between AKI and IL-6