Page 80 - Read Online
P. 80
Cordero et al. Bioresorbable scaffolds in acute coronary syndrome
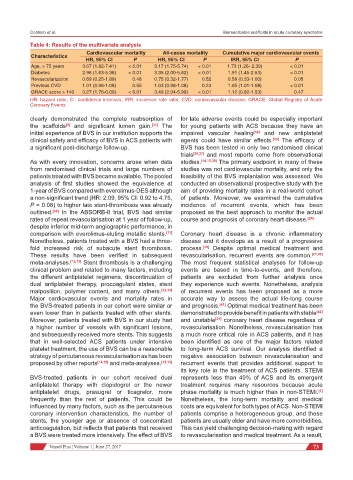
Table 4: Results of the multivariate analysis
Cardiovascular mortality All-cause mortality Cumulative major cardiovascular events
Characteristics
HR, 95% CI P HR, 95% CI P IRR, 95% CI P
Age, > 75 years 3.67 (1.82-7.41) < 0.01 3.17 (1.75-5.74) < 0.01 1.73 (1.26- 2.39) < 0.01
Diabetes 2.96 (1.63-5.36) < 0.01 3.35 (2.00-5.62) < 0.01 1.91 (1.45-2.53) < 0.01
Revascularization 0.69 (0.25-1.89) 0.48 0.75 (0.32-1.77) 0.52 0.58 (0.33-1.00) 0.05
Previous CVD 1.01 (0.96-1.08) 0.55 1.03 (0.98-1.08) 0.23 1.05 (1.01-1.08) < 0.01
GRACE score > 140 3.27 (1.76-6.09) < 0.01 3.49 (2.04-5.99) < 0.01 1.12 (0.82-1.53) 0.47
HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence intervals; IRR: incidence rate ratio; CVD: cardiovascular disease; GRACE: Global Registry of Acute
Coronary Events
clearly demonstrated the complete reabsorption of for late adverse events could be especially important
the scaffolds and significant lumen gain. [31] The for young patients with ACS because they have an
[9]
initial experience of BVS in our institution supports the impaired vascular healing [34] and new antiplatelet
clinical safety and efficacy of BVS in ACS patients with agents could have similar effects. [35] The efficacy of
a significant post-discharge follow-up. BVS has been tested in only two randomised clinical
trials [36,37] and most reports come from observational
As with every innovation, concerns arose when data studies. [14,15,38] The primary endpoint in many of these
from randomised clinical trials and large numbers of studies was not cardiovascular mortality, and only the
patients treated with BVS became available. The pooled feasibility of the BVS implantation was assessed. We
analysis of first studies showed the equivalence at conducted an observational prospective study with the
1-year of BVS compared with everolimus-DES although aim of providing mortality rates in a real-world cohort
a non-significant trend (HR: 2.09, 95% CI: 0.92 to 4.75, of patients. Moreover, we examined the cumulative
P = 0.08) to higher late stent-thrombosis was already incidence of recurrent events, which has been
outlined. [30] In the ABSORB-II trial, BVS had similar proposed as the best approach to monitor the actual
rates of repeat revascularisation at 1 year of follow-up, course and prognosis of coronary heart disease. [24]
despite inferior mid-term angiographic performance, in
comparison with everolimus-eluting metallic stents. [11] Coronary heart disease is a chronic inflammatory
Nonetheless, patients treated with a BVS had a three- disease and it develops as a result of a progressive
fold increased risk of subacute stent thrombosis. process. [39] Despite optimal medical treatment and
These results have been verified in subsequent revascularisation, recurrent events are common. [21,40]
meta-analyses. [12,13] Stent thrombosis is a challenging The most frequent statistical analyses for follow-up
clinical problem and related to many factors, including events are based in time-to-events, and therefore,
the different antiplatelet regimens, discontinuation of patients are excluded from further analysis once
dual antiplatelet therapy, procoagulant states, stent they experience such events. Nonetheless, analysis
malposition, polymer content, and many others. [32,33] of recurrent events has been proposed as a more
Major cardiovascular events and mortality rates in accurate way to assess the actual life-long course
the BVS-treated patients in our cohort were similar or and prognosis. [41] Optimal medical treatment has been
even lower than in patients treated with other stents. demonstrated to provide benefit in patients with stable [42]
Moreover, patients treated with BVS in our study had and unstable [21] coronary heart disease regardless of
a higher number of vessels with significant lesions, revascularisation. Nonetheless, revascularisation has
and subsequently received more stents. This suggests a much more critical role in ACS patients, and it has
that in well-selected ACS patients under intensive been identified as one of the major factors related
platelet treatment, the use of BVS can be a reasonable to long-term ACS survival. Our analysis identified a
strategy of percutaneous revascularisation as has been negative association between revascularisation and
proposed by other reports [14,15] and meta-analyses. [12,13] recurrent events that provides additional support to
its key role in the treatment of ACS patients. STEMI
BVS-treated patients in our cohort received dual represents less than 40% of ACS and its emergent
antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel or the newer treatment requires many resources because acute
antiplatelet drugs, prasugrel or ticagrelor, more phase mortality is much higher than in non-STEMI.
[1]
frequently than the rest of patients. This could be Nonetheless, the long-term mortality and medical
influenced by many factors, such as the percutaneous costs are equivalent for both types of ACS. Non-STEMI
coronary intervention characteristics, the number of patients comprise a heterogeneous group, and these
stents, the younger age or absence of concomitant patients are usually older and have more comorbidities.
anticoagulation, but reflects that patients that received This can yield challenging decision-making with regard
a BVS were treated more intensively. The effect of BVS to revascularisation and medical treatment. As a result,
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 27, 2017 73