Page 252 - Read Online
P. 252
Singh et al. Sternal fixation in a diabetic patient
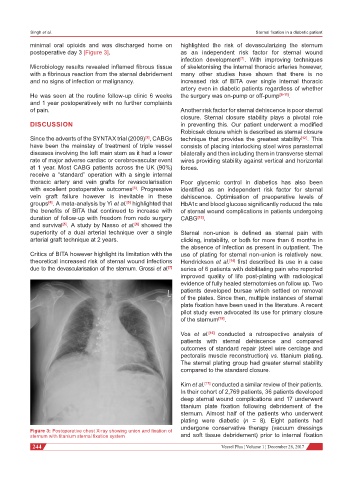
minimal oral opioids and was discharged home on highlighted the risk of devascularizing the sternum
postoperative day 3 [Figure 3]. as an independent risk factor for sternal wound
infection development . With improving techniques
[7]
Microbiology results revealed inflamed fibrous tissue of skeletonising the internal thoracic arteries however,
with a fibrinous reaction from the sternal debridement many other studies have shown that there is no
and no signs of infection or malignancy. increased risk of BITA over single internal thoracic
artery even in diabetic patients regardless of whether
He was seen at the routine follow-up clinic 6 weeks the surgery was on-pump or off-pump [8-11] .
and 1 year postoperatively with no further complaints
of pain. Another risk factor for sternal dehiscence is poor sternal
closure. Sternal closure stability plays a pivotal role
DISCUSSION in preventing this. Our patient underwent a modified
Robicsek closure which is described as sternal closure
Since the advents of the SYNTAX trial (2009) , CABGs technique that provides the greatest stability [12] . This
[2]
have been the mainstay of treatment of triple vessel consists of placing interlocking steel wires parasternal
diseases involving the left main stem as it had a lower bilaterally and then including them in transverse sternal
rate of major adverse cardiac or cerebrovascular event wires providing stability against vertical and horizontal
at 1 year. Most CABG patients across the UK (90%) forces.
receive a “standard” operation with a single internal
thoracic artery and vein grafts for revascularisation Poor glycemic control in diabetics has also been
with excellent postoperative outcomes . Progressive identified as an independent risk factor for sternal
[3]
vein graft failure however is inevitable in these dehiscence. Optimisation of preoperative levels of
[4]
[5]
groups . A meta-analysis by Yi et al. highlighted that HbA1c and blood glucose significantly reduced the rate
the benefits of BITA that continued to increase with of sternal wound complications in patients undergoing
duration of follow-up with freedom from redo surgery CABG [13] .
and survival . A study by Nasso et al. showed the
[6]
[5]
superiority of a dual arterial technique over a single Sternal non-union is defined as sternal pain with
arterial graft technique at 2 years. clicking, instability, or both for more than 6 months in
the absence of infection as present in outpatient. The
Critics of BITA however highlight its limitation with the use of plating for sternal non-union is relatively new.
theoretical increased risk of sternal wound infections Hendrickson et al. [14] first described its use in a case
due to the devascularisation of the sternum. Grossi et al. series of 6 patients with debilitating pain who reported
[7]
improved quality of life post-plating with radiological
evidence of fully healed sternotomies on follow up. Two
patients developed bursae which settled on removal
of the plates. Since then, multiple instances of sternal
plate fixation have been used in the literature. A recent
pilot study even advocated its use for primary closure
of the sternum [15] .
Vos et al. [16] conducted a retrospective analysis of
patients with sternal dehiscence and compared
outcomes of standard repair (steel wire cerclage and
pectoralis muscle reconstruction) vs. titanium plating.
The sternal plating group had greater sternal stability
compared to the standard closure.
Kim et al. [17] conducted a similar review of their patients.
In their cohort of 2,769 patients, 36 patients developed
deep sternal wound complications and 17 underwent
titanium plate fixation following debridement of the
sternum. Almost half of the patients who underwent
plating were diabetic (n = 8). Eight patients had
undergone conservative therapy (vacuum dressings
Figure 3: Postoperative chest X-ray showing union and fixation of
sternum with titanium sternal fixation system and soft tissue debridement) prior to internal fixation
244 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017