Page 148 - Read Online
P. 148
Wu et al. Mast cells and vein graft remodelling
DISCUSSION covalently binds to the positively charged tropoelastin
to accelerate tropoelastin coacervation and elastic
This study demonstrates firstly that perivascular mast fibre formation. [22-24] However, the very short half-
cells elevate neointimal elastin deposition under both life of heparin limits its pharmacological potency for
normolipidaemic and hyperlipidaemic conditions, and therapeutic purposes. Only continuous intravenous
[25]
secondly that they suppress neointimal thickening in delivery, [26-28] but not short term treatment, inhibited
[29]
hyperlipidaemic mice possibly via down regulation of neointima thickening. Interestingly, perivascular
cell proliferation within the vein graft. delivery of heparin required a much smaller dose
and was more effective in suppression of neointima
Elastin is one of the fundamental structural proteins hyperplasia, [20,25] which matches the source of
of the arterial wall that regulates vascular elasticity endogenous heparin from perivascular mast cells.
and stabilises smooth muscle cells. The present Thirdly, mast cell granules are enriched with heparin
[18]
study demonstrates that mast cells play a previously and the heparin-based particles are capable of
unrecognised role in promotion of elastin deposition long distance travel within tissue which makes
[30]
during vein graft remodelling. The causality is perivascular mast cells an ideal and indeed the only
demonstrated by the data showing that mast cell source for continuous heparin supply to assist vascular
deficiency reduced, and mast cell reconstitution elastogenesis.
rescued, elastin deposition in the vein graft.
Although the exact mechanism of how mast cells It is intriguing that mast cell-dependent elastin
regulate elastin deposition is not yet clear, there is deposition had a divergent impact on neointimal
a consensus within the literature that heparin is the hyperplasia in normolipidaemic and hyperlipidaemic
potential mediator. The evidence for the involvement vein grafts. This could be a consequence of the
of heparin is three-fold. Firstly, mast cells are the only different dynamics of neointima formation and vascular
cell type that produces heparin in vivo. Secondly, matrix remodelling. In normolipidaemic mice, the
[19]
heparin is known to promote elastogenesis and neointima formation is driven by acute inflammation
supress neointima hyperplasia in injured arteries and proliferation which peak within one week and
and vascular grafts. [20,21] Being the most negatively are complete by 2 weeks. [13,31] During the 3rd and
charged molecule in biological systems, heparin 4th weeks, the neointimal proliferation decreases
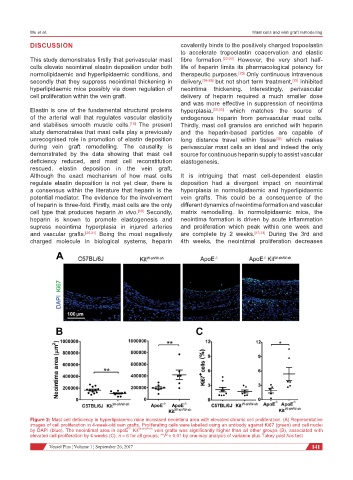
Figure 2: Mast cell deficiency in hyperlipidaemic mice increased neointima area with elevated chronic cell proliferation. (A) Representative
images of cell proliferation in 4-week-old vein grafts. Proliferating cells were labelled using an antibody against Ki67 (green) and cell nuclei
by DAPI (blue). The neointimal area in apoE Kit W-sh/W-sh vein grafts was significantly higher than all other groups (B), associated with
-/-
elevated cell proliferation by 4 weeks (C). n > 6 for all groups; **P < 0.01 by one-way analysis of variance plus Tukey post hoc test
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ September 26, 2017 141