Page 140 - Read Online
P. 140
Gowdar et al. Diabetes mellitus and takotsubo cardiomyopathy
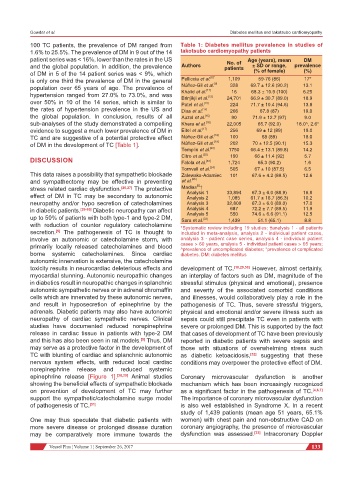
100 TC patients, the prevalence of DM ranged from Table 1: Diabetes mellitus prevalence in studies of
1.6% to 25.5%. The prevalence of DM in 9 out of the 14 takotsubo cardiomyopathy patients
patient series was < 16%, lower than the rates in the US No. of Age (years), mean DM
and the global population. In addition, the prevalence Authors patients ± SD or range, prevalence
of DM in 5 of the 14 patient series was < 9%, which (% of female) (%)
is only one third the prevalence of DM in the general Pelliccia et al. [8]* [9] 1,109 59-76 (86) 17*
population over 65 years of age. The prevalence of Núñez-Gil et al. 328 69.7 ± 12.6 (90.2) 13.1
[11]
68.3 ± 10.9 (100)
16
hypertension ranged from 27.0% to 73.0%, and was Khalid et al. [12] 24,701 66.9 ± 30.7 (89.0) 6.25
Brinjikji et al.
18.9
over 50% in 10 of the 14 series, which is similar to Patel et al. [13] 224 71.7 ± 10.4 (94.6) 13.8
the rates of hypertension prevalence in the US and Dias et al. [14] 206 67.8 (87) 19.0
the global population. In conclusion, results of all Auzal et al. [15] 90 71.9 ± 12.7 (97) 9.0
sub-analyses of the study demonstrated a compelling Khera et al. [16] 22,005 65.7 (92.0) 18.0^, 2.6°
evidence to suggest a much lower prevalence of DM in Eitel et al. [17] 256 69 ± 12 (89) 19.0
TC and are suggestive of a potential protective effect Núñez-Gil et al. [18] 100 68 (89) 18.0
of DM in the development of TC [Table 1]. Núñez-Gil et al. [19] 202 70 ± 12.5 (90.1) 15.3
Templin et al. [20] 1750 66.4 ± 13.1 (89.8) 14.2
Citro et al. [22] 190 66 ± 11.4 (92) 5.7
DISCUSSION Falola et al. [23] 1,724 65.3 (90.2) 1.6
Tornvall et al. [24] 505 67 ± 10 (87.5) 6.5
This data raises a possibility that sympathetic blockade Zalewska-Adamiec 101 67.6 ± 4.2 (89.5) 12.6
and sympathectomy may be effective in preventing et al. [25]
[5]
stress related cardiac dysfunction. [26,27] The protective Madias †
67.3 ± 6.0 (88.9)
effect of DM in TC may be secondary to autonomic Analysis 1 33,894 61.7 ± 16.7 (86.3) 16.8
1,085
10.2
Analysis 2
neuropathy and/or hypo secretion of catecholamines Analysis 3 32,809 67.3 ± 6.0 (89.0) 17.0
in diabetic patients. [26-30] Diabetic neuropathy can affect Analysis 4 687 72.2 ± 7.7 (89.5) 11.9
Analysis 5
74.6 ± 6.6 (91.1)
550
12.5
up to 50% of patients with both type-1 and type-2 DM, Sara et al. [33] 1,439 51.1 (65.1) 8.8
with reduction of counter regulatory catecholamine *Systematic review including 19 studies; †analysis 1 - all patients
secretion. The pathogenesis of TC is thought to included in meta-analysis, analysis 2 - individual patient cases,
[5]
involve an autonomic or catecholamine storm, with analysis 3 - patient case series, analysis 4 - individual patient
primarily locally released catecholamines and blood cases > 60 years, analysis 5 - individual patient cases > 65 years;
^prevalence of uncomplicated diabetes; °prevalence of complicated
borne systemic catecholamines. Since cardiac diabetes. DM: diabetes mellitus
autonomic innervation is extensive, the catecholamine
toxicity results in neurocardiac deleterious effects and development of TC. [10,29,30] However, almost certainly,
myocardial stunning. Autonomic neuropathic changes an interplay of factors such as DM, magnitude of the
in diabetics result in neuropathic changes in splanchnic stressful stimulus (physical and emotional), presence
autonomic sympathetic nerves or in adrenal chromaffin and severity of the associated comorbid conditions
cells which are innervated by these autonomic nerves, and illnesses, would collaboratively play a role in the
and result in hyposecretion of epinephrine by the pathogenesis of TC. Thus, severe stressful triggers,
adrenals. Diabetic patients may also have autonomic physical and emotional and/or severe illness such as
neuropathy of cardiac sympathetic nerves. Clinical sepsis could still precipitate TC even in patients with
studies have documented reduced norepinephrine severe or prolonged DM. This is supported by the fact
release in cardiac tissue in patients with type-2 DM that cases of development of TC have been previously
and this has also been seen in rat models. Thus, DM reported in diabetic patients with severe sepsis and
[5]
may serve as a protective factor in the development of those with situations of overwhelming stress such
TC with blunting of cardiac and splanchnic autonomic as diabetic ketoacidosis, [32] suggesting that these
nervous system effects, with reduced local cardiac conditions may overpower the protective effect of DM.
norepinephrine release and reduced systemic
epinephrine release [Figure 1]. [28,29] Animal studies Coronary microvascular dysfunction is another
showing the beneficial effects of sympathetic blockade mechanism which has been increasingly recognized
on prevention of development of TC may further as a significant factor in the pathogenesis of TC. [4,6,7]
support the sympathetic/catecholamine surge model The importance of coronary microvascular dysfunction
of pathogenesis of TC. [31] is also well established in Syndrome X. In a recent
study of 1,439 patients (mean age 51 years, 65.1%
One may thus speculate that diabetic patients with women) with chest pain and non-obstructive CAD on
more severe disease or prolonged disease duration coronary angiography, the presence of microvascular
may be comparatively more immune towards the dysfunction was assessed. [33] Intracoronary Doppler
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ September 26, 2017 133