Page 180 - Read Online
P. 180
Page 6 of 13 Misra et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:32 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.104
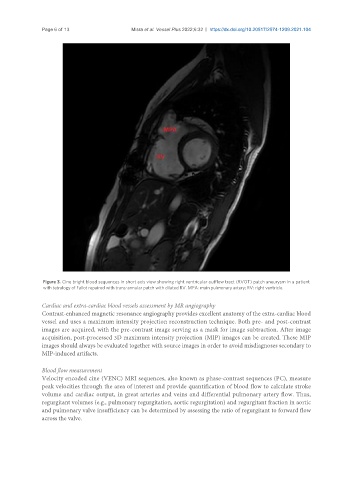
Figure 3. Cine bright blood sequences in short axis view showing right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) patch aneurysm in a patient
with tetralogy of Fallot repaired with trans-annular patch with dilated RV. MPA: main pulmonary artery; RV: right ventricle.
Cardiac and extra-cardiac blood vessels assessment by MR angiography
Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography provides excellent anatomy of the extra-cardiac blood
vessel and uses a maximum intensity projection reconstruction technique. Both pre- and post-contrast
images are acquired, with the pre-contrast image serving as a mask for image subtraction. After image
acquisition, post-processed 3D maximum intensity projection (MIP) images can be created. These MIP
images should always be evaluated together with source images in order to avoid misdiagnoses secondary to
MIP-induced artifacts.
Blood flow measurement
Velocity encoded cine (VENC) MRI sequences, also known as phase-contrast sequences (PC), measure
peak velocities through the area of interest and provide quantification of blood flow to calculate stroke
volume and cardiac output, in great arteries and veins and differential pulmonary artery flow. Thus,
regurgitant volumes (e.g., pulmonary regurgitation, aortic regurgitation) and regurgitant fraction in aortic
and pulmonary valve insufficiency can be determined by assessing the ratio of regurgitant to forward flow
across the valve.