Page 42 - Read Online
P. 42
Page 8 of 20 Pardo et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:36 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.120
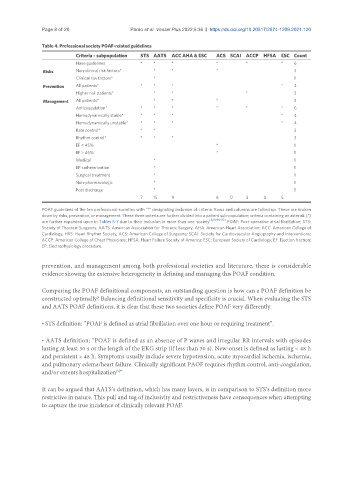
Table 4. Professional society POAF-related guidelines
Criteria - subpopulation STS AATS ACC AHA & ESC ACS SCAI ACCP HFSA ESC Count
Have guidelines * * * * * * 6
Risks Non-clinical risk factors* * * * 3
Clinical risk factors* * 1
Prevention All patients* * * * * 4
Higher risk patients* * * * 3
Management All patients* * * * 3
Anticoagulation* * * * * * * 6
Hemodynamically stable* * * * * 4
Hemodynamically unstable* * * * * 4
Rate control* * * 2
Rhythm control* * * * 3
EF < 45% * 1
EF > 45% * 1
Medical * 1
EP catheterization * 1
Surgical treatment * 1
Non-pharmacologic * 1
Post discharge * 1
7 15 9 6 0 3 0 5
POAF guidelines of the ten professional societies with “*” designating inclusion of criteria. Rows and columns are tallied up. These are broken
down by risks, prevention, or management. These three criteria are further divided into a patient sub-population; criteria containing an asterisk (*)
are further expanded upon in Tables 5-7 due to their inclusion in more than one society [8,10,90-93] . POAF: Post-operative atrial fibrillation; STS:
Society of Thoracic Surgeons; AATS: American Association for Thoracic Surgery; AHA: American Heart Association; ACC: American College of
Cardiology; HRS: Heart Rhythm Society; ACS: American College of Surgeons; SCAI: Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions;
ACCP: American College of Chest Physicians; HFSA: Heart Failure Society of America; ESC: European Society of Cardiology; EF: Ejection fraction;
EP: Electrophysiology procedure.
prevention, and management among both professional societies and literature, there is considerable
evidence showing the extensive heterogeneity in defining and managing this POAF condition.
Comparing the POAF definitional components, an outstanding question is how can a POAF definition be
constructed optimally? Balancing definitional sensitivity and specificity is crucial. When evaluating the STS
and AATS POAF definitions, it is clear that these two societies define POAF very differently.
• STS definition: “POAF is defined as atrial fibrillation over one hour or requiring treatment”.
• AATS definition: “POAF is defined as an absence of P waves and irregular RR intervals with episodes
lasting at least 30 s or the length of the EKG strip (if less than 30 s). New-onset is defined as lasting < 48 h
and persistent > 48 h. Symptoms usually include severe hypotension, acute myocardial ischemia, ischemia,
and pulmonary edema/heart failure. Clinically significant PAOF requires rhythm control, anti-coagulation,
[8]
and/or extents hospitalization ”.
It can be argued that AATS’s definition, which has many layers, is in comparison to STS’s definition more
restrictive in nature. This pull and tug of inclusivity and restrictiveness have consequences when attempting
to capture the true incidence of clinically relevant POAF.