Page 69 - Read Online
P. 69
Mattana et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:13 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.87 Page 7 of 11
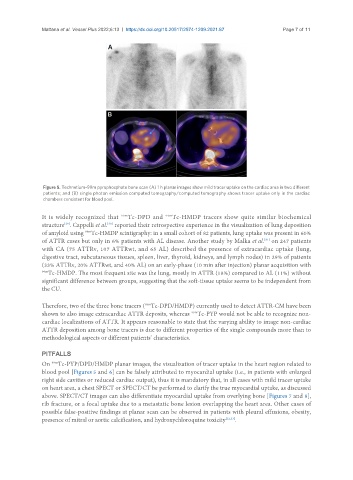
Figure 5. Technetium-99m pyrophosphate bone scan (A) 1 h planar images show mild tracer uptake on the cardiac area in two different
patients; and (B) single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography shows tracer uptake only in the cardiac
chambers consistent for blood pool.
It is widely recognized that 99m Tc-DPD and 99m Tc-HMDP tracers show quite similar biochemical
structure . Cappelli et al. reported their retrospective experience in the visualization of lung deposition
[29]
[30]
99m
of amyloid using Tc-HMDP scintigraphy: in a small cohort of 82 patients, lung uptake was present in 60%
[31]
of ATTR cases but only in 6% patients with AL disease. Another study by Malka et al. on 247 patients
with CA (75 ATTRv, 107 ATTRwt, and 65 AL) described the presence of extracardiac uptake (lung,
digestive tract, subcutaneous tissues, spleen, liver, thyroid, kidneys, and lymph nodes) in 29% of patients
(33% ATTRv, 20% ATTRwt, and 40% AL) on an early-phase (10 min after injection) planar acquisition with
99m Tc-HMDP. The most frequent site was the lung, mostly in ATTR (18%) compared to AL (11%) without
significant difference between groups, suggesting that the soft-tissue uptake seems to be independent from
the CU.
Therefore, two of the three bone tracers ( Tc-DPD/HMDP) currently used to detect ATTR-CM have been
99m
shown to also image extracardiac ATTR deposits, whereas Tc-PYP would not be able to recognize non-
99m
cardiac localizations of ATTR. It appears reasonable to state that the varying ability to image non-cardiac
ATTR deposition among bone tracers is due to different properties of the single compounds more than to
methodological aspects or different patients’ characteristics.
PITFALLS
99m
On Tc-PYP/DPD/HMDP planar images, the visualization of tracer uptake in the heart region related to
blood pool [Figures 5 and 6] can be falsely attributed to myocardial uptake (i.e., in patients with enlarged
right side cavities or reduced cardiac output), thus it is mandatory that, in all cases with mild tracer uptake
on heart area, a chest SPECT or SPECT/CT be performed to clarify the true myocardial uptake, as discussed
above. SPECT/CT images can also differentiate myocardial uptake from overlying bone [Figures 7 and 8],
rib fracture, or a focal uptake due to a metastatic bone lesion overlapping the heart area. Other cases of
possible false-positive findings at planar scan can be observed in patients with pleural effusions, obesity,
presence of mitral or aortic calcification, and hydroxychloroquine toxicity [32,33] .