Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Licordari et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:12 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.86 Page 5 of 10
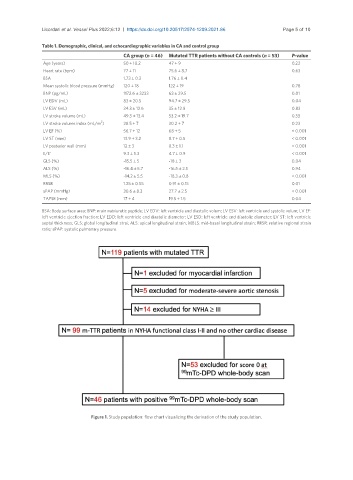
Table 1. Demographic, clinical, and echocardiographic variables in CA and control group
CA group (n = 46) Mutated TTR patients without CA controls (n = 53) P-value
Age (years) 50 ± 10.2 47 ± 9 0.22
Heart rate (bpm) 77 ± 11 75.6 ± 8.7 0.63
BSA 1.73 ± 0.3 1.76 ± 0.4
Mean systolic blood pressure (mmHg) 120 ± 18 122 ± 19 0.78
BNP (pg/mL) 1172.6 ± 3233 63 ± 29.5 0.01
LV EDV (mL) 83 ± 20.5 94.7 ± 29.5 0.04
LV ESV (mL) 34.3 ± 12.6 35 ± 12.8 0.83
LV stroke volume (mL) 49.3 ± 13.4 53.2 ± 19.7 0.33
2
LV stroke volume index (mL/m ) 28.5 ± 7 30.2 ± 7 0.23
LV EF (%) 56.7 ± 12 68 ± 5 < 0.001
LV ST (mm) 13.9 ± 3.2 8.7 ± 0.5 < 0.001
LV posterior wall (mm) 12 ± 3 8.3 ± 1.1 < 0.001
E/E’ 9.3 ± 5.3 4.7 ± 0.9 < 0.001
GLS (%) -15.5 ± 5 -18 ± 3 0.04
ALS (%) -16.4 ± 5.7 -16.5 ± 2.5 0.94
MLS (%) -14.2 ± 5.5 -18.3 ± 0.8 < 0.001
RRSR 1.25 ± 0.55 0.91 ± 0.15 0.01
sPAP (mmHg) 30.6 ± 8.3 27.7 ± 2.5 < 0.001
TAPSE (mm) 17 ± 4 19.5 ± 1.5 0.04
BSA: Body surface area; BNP: nrain natriuretic peptide; LV EDV: left ventricle end diastolic volum; LV ESV: left ventricle end systolic volum; LV EF:
left ventricle ejection fraction; LV EDD: left ventricle end diastolic diameter; LV ESD: left ventricle end diastolic diameter; LV ST: left ventricle
septal thickness; GLS: global longitudinal strai; ALS: apical longitudinal strain; MBLS: mid-basal longitudinal strain; RRSR: relative regional strain
ratio; sPAP: systolic pulmonary pressure.
Figure 1. Study population: flow chart visualizing the derivation of the study population.