Page 14 - Read Online
P. 14
Page 8 of 11 Genovesi et al. Vessel Plus 2021;5:50 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.67
Table 1. Main characteristics and differences among the most commonly used radiopharmaceuticals for CA
Time between injection and
Radiopharmaceutical Activity Image type Contraindications
acquisition
99mTc-PYP 370-740 1 h (3 h if needed) Planar and SPECT (or Pregnancy or breast-feeding
MBq SPECT-CT)
99mTc-DPD 370-740 2-3 h Planar and SPECT (or Pregnancy or breast-feeding
MBq SPECT-CT)
99mTc-HMDP 370-740 2-3 h Planar and SPECT (or Pregnancy or breast-feeding
MBq SPECT-CT)
18F-Florbetaben 111-185 MBq 1-2 h Static PET-CT Pregnancy, breast-feeding, severe renal
and/or liver failure
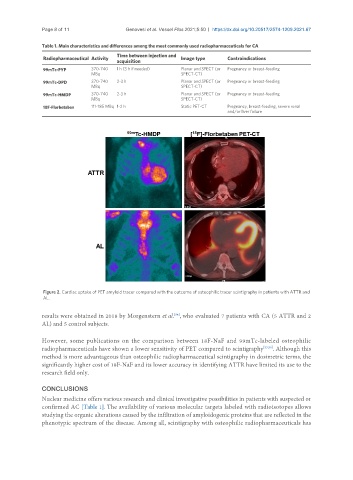
Figure 2. Cardiac uptake of PET amyloid tracer compared with the outcome of osteophilic tracer scintigraphy in patients with ATTR and
AL.
[54]
results were obtained in 2018 by Morgenstern et al. , who evaluated 7 patients with CA (5 ATTR and 2
AL) and 5 control subjects.
However, some publications on the comparison between 18F-NaF and 99mTc-labeled osteophilic
radiopharmaceuticals have shown a lower sensitivity of PET compared to scintigraphy [55,56] . Although this
method is more advantageous than osteophilic radiopharmaceutical scintigraphy in dosimetric terms, the
significantly higher cost of 18F-NaF and its lower accuracy in identifying ATTR have limited its use to the
research field only.
CONCLUSIONS
Nuclear medicine offers various research and clinical investigative possibilities in patients with suspected or
confirmed AC [Table 1]. The availability of various molecular targets labeled with radioisotopes allows
studying the organic alterations caused by the infiltration of amyloidogenic proteins that are reflected in the
phenotypic spectrum of the disease. Among all, scintigraphy with osteophilic radiopharmaceuticals has