Page 13 - Read Online
P. 13
Genovesi et al. Vessel Plus 2021;5:50 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.67 Page 7 of 11
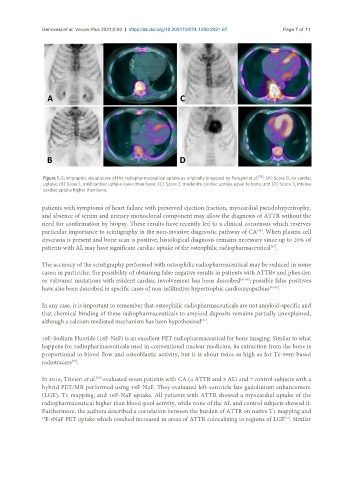
Figure 1. Scintigraphic visual score of the radiopharmaceutical uptake as originally proposed by Perugini et al. [38] : (A) Score 0, no cardiac
uptake; (B) Score 1, mild cardiac uptake lower than bone; (C) Score 2, moderate cardiac uptake equal to bone; and (D) Score 3, intense
cardiac uptake higher than bone.
patients with symptoms of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, myocardial pseudohypertrophy,
and absence of serum and urinary monoclonal component may allow the diagnosis of ATTR without the
need for confirmation by biopsy. These results have recently led to a clinical consensus which reserves
[46]
particular importance to scintigraphy in the non-invasive diagnostic pathway of CA . When plasma cell
dyscrasia is present and bone scan is positive, histological diagnosis remains necessary since up to 20% of
patients with AL may have significant cardiac uptake of the osteophilic radiopharmaceutical .
[45]
The accuracy of the scintigraphy performed with osteophilic radiopharmaceutical may be reduced in some
cases; in particular, the possibility of obtaining false negative results in patients with ATTRv and phe64leu
or val30met mutations with evident cardiac involvement has been described [47,48] ; possible false positives
have also been described in specific cases of non-infiltrative hypertrophic cardiomyopathies [49,50] .
In any case, it is important to remember that osteophilic radiopharmaceuticals are not amyloid-specific and
that chemical binding of these radiopharmaceuticals to amyloid deposits remains partially unexplained,
although a calcium mediated mechanism has been hypothesized .
[51]
18F-Sodium Fluoride (18F-NaF) is an excellent PET radiopharmaceutical for bone imaging. Similar to what
happens for radiopharmaceuticals used in conventional nuclear medicine, its extraction from the bone is
proportional to blood flow and osteoblastic activity, but it is about twice as high as for Tc-99m-based
radiotracers .
[52]
[53]
In 2016, Trivieri et al. evaluated seven patients with CA (4 ATTR and 3 AL) and 7 control subjects with a
hybrid PET/MR performed using 18F-NaF. They evaluated left-ventricle late gadolinium enhancement
(LGE), T1 mapping, and 18F-NaF uptake. All patients with ATTR showed a myocardial uptake of the
radiopharmaceutical higher than blood-pool activity, while none of the AL and control subjects showed it.
Furthermore, the authors described a correlation between the burden of ATTR on native T1 mapping and
[53]
18 F-sNaF PET uptake which resulted increased in areas of ATTR colocalizing to regions of LGE . Similar