Page 133 - Read Online
P. 133
De Gaspari et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:57 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2022.05 Page 7 of 13
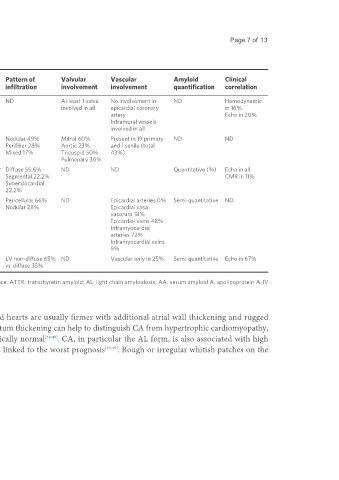
Table 2. Whole heart-pathology studies on cardiac amyloidosis: literature review
Mean age,
Author, year ref Source N. years Amyloid Amyloid localization Pattern of Valvular Vascular Amyloid Clinical
cases typing infiltration involvement involvement quantification correlation
(range)
Roberts and Waller, Autopsy 54 64 (21-97) ND Interstitium and endocardium ND At least 1 valve No involvement in ND Hemodynamic
[39]
1983 (including in all; always 1 or both atria involved in all epicardial coronary in 16%
[38]
cases from ) artery Echo in 20%
Intramural vessels
involved in all
[40]
Smith et al. , 1984 Autopsy 47 Primary 57.6 Primary vs. Endocardial 70% Nodular 49% Mitral 60% Present in 19 primary ND ND
(35-83) senile Pericardial 36% Perifiber 28% Aortic 23% and 1 senile (total
Senile Left atrium 91% Mixed 17% Tricuspid 50% 43%)
83 (70-89) Right atrium 81% Pulmonary 30%
[41]
Leone et al. , 2012 Autopsy 9 56 (54-60) 5 ATTR Computed analysis: trabecular Diffuse 55.6% ND ND Quantitative (%) Echo in all
and HT (unspecified) and subendocardial layers Segmental 22.2% CMR in 11%
4 AL most infiltrated Subendocardial
22.2%
[42]
Larsen et al. , 2016 Autopsy 108 75 (31-89) 60 ATTRwt Interstitium 85% Pericellular 66% ND Epicardial arteries 0% Semi-quantitative ND
44 AL (32 λ, 12 Endocardium 41% Nodular 28% Epicardial vasa
κ) vasorum 18%
2 AA Epicardial veins 48%
1 AApoAIV Intramyocardial
1 AL + AH arteries 72%
Intramyocardial veins
9%
[43]
Porcari et al. , 2021 Autopsy 24 86 (84-91) 12 AL Interstitium in 75% LV non-diffuse 65% ND Vascular only in 25% Semi-quantitative Echo in 67%
12 ATTR vs. diffuse 35%
ND: Not disposable; HT: heart transplantation; echo: echocardiography; CMR: cardiac magnetic resonance; ATTR: transthyretin amyloid; AL: light chain amyloidosis; AA: serum amyloid A, apolipoprotein A-IV
amyloidosis; AH: heavy chain amyloidosis.
[45]
1 kg . Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the major mimicker [46,47] , but amyloid hearts are usually firmer with additional atrial wall thickening and rugged
appearance of the endocardial surface. In addition, the marker of interatrial septum thickening can help to distinguish CA from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,
particularly in the clinical setting . In some cases, hearts can be macroscopically normal [39,40] . CA, in particular the AL form, is also associated with high
[48]
frequency of intracardiac thrombi, most commonly localized in the atria and linked to the worst prognosis [39,49] . Rough or irregular whitish patches on the
external surface of the heart may indicate epicardial involvement.