Page 128 - Read Online
P. 128
De Gaspari et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:57 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2022.05 Page 3 of 13
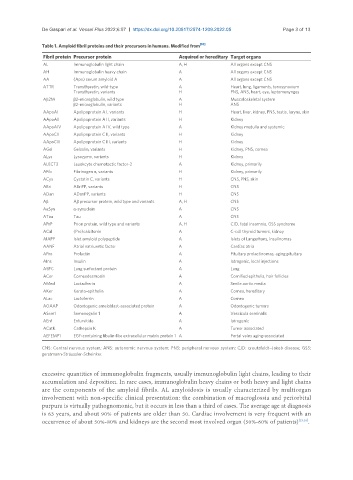
Table 1. Amyloid fibril proteins and their precursors in humans. Modified from [10]
Fibril protein Precursor protein Acquired or hereditary Target organs
AL Immunoglobulin light chain A, H All organs except CNS
AH Immunoglobulin heavy chain A All organs except CNS
AA (Apo) serum amyloid A A All organs except CNS
ATTR Transthyretin, wild-type A Heart, lung, ligaments, tenosynovium
Transthyretin, variants H PNS, ANS, heart, eye, leptomenynges
Aβ2M β2-microglobulin, wild type A Muscoloskeletal system
β2-microglobulin, variants H ANS
AApoAI Apolipoprotein A I, variants H Heart, liver, kidney, PNS, testis, larynx, skin
AApoAII Apolipoprotein A II, variants H Kidney
AApoAIV Apolipoprotein A IV, wild type A Kidney medulla and systemic
AApoCII Apolipoprotein C II, variants H Kidney
AApoCIII Apolipoprotein C III, variants H Kidney
AGel Gelsolin, variants H Kidney, PNS, cornea
ALys Lysozyme, variants H Kidney
ALECT2 Leuokcyte chemotactic factor-2 A Kidney, primarily
AFib Fibrinogen α, variants H Kidney, primarily
ACys Cystatin C, variants H CNS, PNS, skin
ABri ABriPP, variants H CNS
ADan ADanPP, variants H CNS
Aβ Aβ precursor protein, wild type and variants A, H CNS
AαSyn α-synuclein A CNS
ATau Tau A CNS
APrP Prion protein, wild type and variants A, H CJD, fatal insomnia, GSS syndrome
ACal (Pro)calcitonin A C-cell thyroid tumors, kidney
AIAPP Islet amyloid polypeptide A Islets of Langerhans, insulinomas
AANF Atrial natriuretic factor A Cardiac atria
APro Prolactin A Pituitary prolactinomas, aging pituitary
AIns Insulin A Iatrogenic, local injections
ASPC Lung surfactant protein A Lung
ACor Corneodesmosin A Cornified epithelia, hair follicles
AMed Lactadherin A Senile aortic media
AKer Kerato-epithelin A Cornea, hereditary
ALac Lactoferrin A Cornea
AOAAP Odontogenic ameloblast-associated protein A Odontogenic tumors
ASem1 Semenogelin 1 A Vescicula seminalis
AEnf Enfurvitide A Iatrogenic
ACatK Cathepsin K A Tumor associated
AEFEMP1 EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 A Portal veins aging-associated
CNS: Central nervous system; ANS: autonomic nervous system; PNS: peripheral nervous system; CJD: creutzfeldt–Jakob disease; GSS:
gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker.
excessive quantities of immunoglobulin fragments, usually immunoglobulin light chains, leading to their
accumulation and deposition. In rare cases, immunoglobulin heavy chains or both heavy and light chains
are the components of the amyloid fibrils. AL amyloidosis is usually characterized by multiorgan
involvement with non-specific clinical presentation: the combination of macroglossia and periorbital
purpura is virtually pathognomonic, but it occurs in less than a third of cases. The average age at diagnosis
is 63 years, and about 90% of patients are older than 50. Cardiac involvement is very frequent with an
occurrence of about 50%-80% and kidneys are the second most involved organ (50%-60% of patients) [15,16] .