Page 192 - Read Online
P. 192
Page 4 of 16 Harik et al. Vessel Plus 2023;7:30 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2023.124
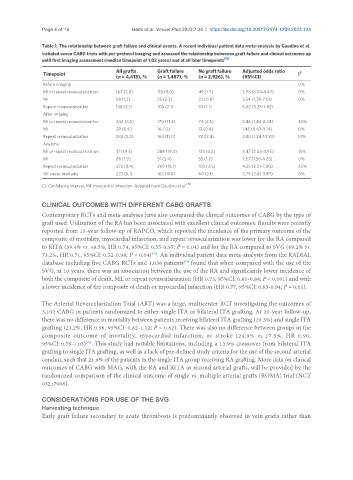
Table 1. The relationship between graft failure and clinical events. A recent individual patient data meta-analysis by Gaudino et al.
included seven CABG trials with per-protocol imaging and assessed the relationship betweeen graft failure and clinical outcomes up
until first imaging assessment (median timepoint of 1.02 years) and at all later timepoints [15]
All grafts Graft failure No graft failure Adjusted odds ratio
Timepoint I 2
(n = 4,413), % (n = 1,487), % (n = 2,926), % (95%CI)
Before imaging 0%
MI or repeat revascularization 167 (3.8) 118 (8.0) 49 (1.7) 3.98 (3.54-4.47) 0%
MI 58 (1.3) 35 (2.3) 23 (0.8) 3.54 (1.78-7.01) 0%
Repeat revascularization 138 (3.1) 105 (7.1) 33 (1.1) 5.02 (3.23-7.82)
After imaging
MI or repeat revascularization 244 (5.5) 170 (11.4) 74 (2.5) 3.46 (1.44-8.34) 43%
MI 28 (0.6) 16 (1.1) 12 (0.4) 1.45 (0.67-3.14) 0%
Repeat revascularization 234 (5.3) 164 (11.0) 70 (2.4) 3.80 (1.24-10.83) 51%
Anytime
MI or repeat revascularization 411 (9.3) 288 (19.4) 123 (4.2) 3.47 (2.43-4.95) 15%
MI 86 (1.9) 51 (3.4) 35 (1.2) 2.57 (1.56-4.25) 0%
Repeat revascularization 372 (8.4) 269 (18.1) 103 (3.5) 4.25 (2.31-7.80) 35%
All-cause mortality 223 (5.1) 163 (11.0) 60 (2.1) 2.79 (2.01-3.89) 0%
[15]
CI: Confidence interval; MI: myocardial infarction. Adapted from Gaudino et al. .
CLINICAL OUTCOMES WITH DIFFERENT CABG GRAFTS
Contemporary RCTs and meta-analyses have also compared the clinical outcomes of CABG by the type of
graft used. Utilization of the RA has been associated with excellent clinical outcomes. Results were recently
reported from 15-year follow-up of RAPCO, which reported the incidence of the primary outcome of the
composite of mortality, myocardial infarction, and repeat revascularization was lower for the RA compared
to RITA (39.4% vs. 48.5%, HR 0.74, 95%CI: 0.55-0.97; P = 0.04) and for the RA compared to SVG (69.2% vs.
73.2%, HR 0.71, 95%CI: 0.52-0.98; P = 0.04) . An individual patient data meta-analysis from the RADIAL
[18]
[19]
database including five CABG RCTs and 1,036 patients found that when compared with the use of the
SVG, at 10 years, there was an association between the use of the RA and significantly lower incidence of
both the composite of death, MI, or repeat revascularization (HR 0.73, 95%CI: 0.61-0.88; P < 0.001) and with
a lower incidence of the composite of death or myocardial infarction (HR 0.77, 95%CI: 0.63-0.94; P = 0.01).
The Arterial Revascularization Trial (ART) was a large, multicenter RCT investigating the outcomes of
3,102 CABG in patients randomized to either single ITA or bilateral ITA grafting. At 10-year follow-up,
there was no difference in mortality between patients receiving bilateral ITA grafting (20.3%) and single ITA
grafting (21.2%, HR 0.96, 95%CI: 0.82-1.12; P = 0.62). There was also no difference between groups in the
composite outcome of mortality, myocardial infarction, or stroke (24.9% vs. 27.3%, HR 0.90,
95%CI: 0.79-1.03) . This study had notable limitations, including a 13.9% crossover from bilateral ITA
[20]
grafting to single ITA grafting, as well as a lack of pre-defined study criteria for the use of the second arterial
conduit, such that 21.8% of the patients in the single ITA group receiving RA grafting. More data on clinical
outcomes of CABG with MAG, with the RA and RITA as second arterial grafts, will be provided by the
randomized comparison of the clinical outcome of single vs. multiple arterial grafts (ROMA) trial (NCT
03217006).
CONSIDERATIONS FOR USE OF THE SVG
Harvesting technique
Early graft failure secondary to acute thrombosis is predominantly observed in vein grafts rather than