Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
Page 6 of 10 Fan et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:43 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.63
Table 1. MA performance of MOF-based MAMs
Dimension Morphology EAB (GHz) RL (dB) Filling ratio (wt.%) Refs.
MAMs
0D Core-shell Ni@C@ZnO 4.1 -55.8 (2.5 mm) 25 40
hollow Co/C 6.8 -52.66 (2.7 mm) 30 45
1D Nanotubes Co/MnO/CNTs 4.5 (1.32 mm) -58.0 35 46
2D Nanosheets N-GN - -54 (2.1 mm) 3 47
3D Flower NCNT/NiCo/C 4.64 -66.1 (1.5 mm) 15 37
aerogel CoNiFe-PBA/GO 6.6 -66.23 (2.6 mm) 1.1 33
MA: Microwave absorption; MOF: Metal-organic framework; MAMs: Microwave absorbing materials; EAB: Effective absorption bandwidth; RL:
Reflection loss; CNT: Carbon nanotube; N-GN: N-doped porous graphene carbon nanonets; NCNT: N-doped CNT; PBA: Prussian blue analog; GO:
Graphene oxide; 0D: Zero-dimensional; 1D: One-dimensional; 2D: Two-dimensional; 3D: Three-dimensional.
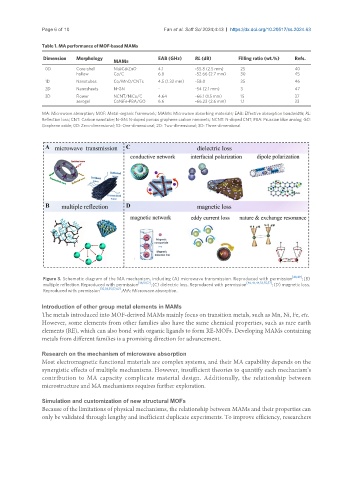
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the MA mechanism, including (A) microwave transmission. Reproduced with permission [48,49] ; (B)
multiple reflection. Reproduced with permission [38,51,52] ; (C) dielectric loss. Reproduced with permission [40,43,44,53,55,57] ; (D) magnetic loss.
Reproduced with permission [35,39,55,57,62] . MA: Microwave absorption.
Introduction of other group metal elements in MAMs
The metals introduced into MOF-derived MAMs mainly focus on transition metals, such as Mn, Ni, Fe, etc.
However, some elements from other families also have the same chemical properties, such as rare earth
elements (RE), which can also bond with organic ligands to form RE-MOFs. Developing MAMs containing
metals from different families is a promising direction for advancement.
Research on the mechanism of microwave absorption
Most electromagnetic functional materials are complex systems, and their MA capability depends on the
synergistic effects of multiple mechanisms. However, insufficient theories to quantify each mechanism's
contribution to MA capacity complicate material design. Additionally, the relationship between
microstructure and MA mechanisms requires further exploration.
Simulation and customization of new structural MOFs
Because of the limitations of physical mechanisms, the relationship between MAMs and their properties can
only be validated through lengthy and inefficient duplicate experiments. To improve efficiency, researchers