Page 60 - Read Online
P. 60
Du et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:35 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.31 Page 3 of 23
Table 1. Advantages, disadvantages, and biomedical applications of different stimuli-responsive hydrogel actuators
Stimulus-responsive Advantages Disadvantages Biomedical applications Ref.
pH (1) High specificity (1) Difficult to biodegrade (1) Cancer treatment [10-14]
(2) Precise release (2) Periodontal disease
(3) Gastrointestinal disease
(4) Periocular disease
(5) Diabetic wound healing
Temperature (1) Easy to control (1) Poor biocompatibility (1) Cancer treatment [15-18]
(2) Simplicity of operator (2) Unable to take active control (2) Periodontal disease
(3) Short response time (3) Periocular disease
(4) Wide application (5) Diabetic wound healing
Electricity (1) Actively controlled (1) Gel fatigues easily (1) Wound healing [19,20]
(2) Can adjust (2) Requirements for instruments (2) Drug delivery
Glucose (1) Good biocompatibility (1) Slow response (1) Periodontal disease [21-23]
(2) Long duration (2) Gel recovery was slower (2) Diabetes mellitus
(3) Diabetic wound healing
Enzyme (1) High efficiency (1) Strict environmental conditions (1) Cancer treatment [24-26]
(2) High specificity (2) Cause needs a prerequisite (2) Periodontal disease
(3) Gastrointestinal disease
Light (1) Safe (1) Difficult to penetrate the tissue (1) Cancer treatment [27,28]
(2) Sensitive (2) Periodontal disease
(3) Low cost
Magnet (1) Actively controlled (1) Not biodegradable (1) Cancer treatment [29,30]
(2) Wireless and remote (2) Drug delivery
Redox (1) Target release (1) Unable to take active control (1) Periodontal disease [31-33]
(2) Gastrointestinal disease
(3) Diabetic wound healing
Ultrasound (1) Safe (1) Destroy the gel structure (1) Gastrointestinal disease [34,35]
(2) Trigger remotely (2) Drug delivery
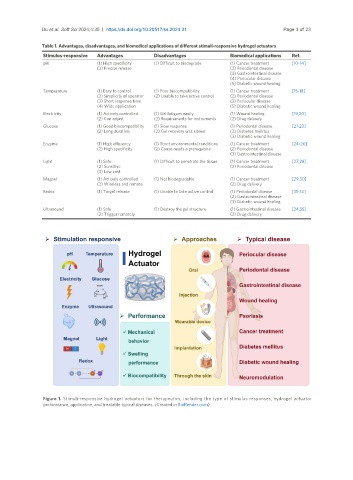
Figure 1. Stimuli-responsive hydrogel actuators for therapeutics, including the type of stimulus responses, hydrogel actuator
performance, application, and treatable typical diseases. (Created in BioRender.com).