Page 50 - Read Online
P. 50
Jung et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:15 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.02 Page 29 of 44
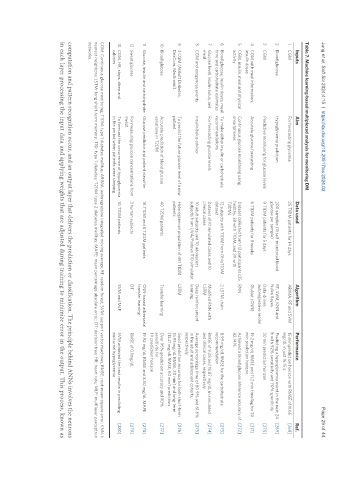
Table 7. Machine learning-based multiplexed analysis for monitoring DM
Inputs Aim Data used Algorithm Performance Ref.
1 CGM For forecasting glycemia 25 T1DM patients for 14 days ARIMA, RF and SVM 15 min prediction horizon with RMSE of 11.65 [268]
mg/dL in just 16.15 s
2 Blood glucose Hypoglycemia prediction 200 samples (11 self-monitored blood RF, SVM, KNN and Predicting a hypoglycemia event in the next 24 [269]
glucose per sample) Naïve Bayes h with 92% sensitivity and 70% specificity
3 CGM Predictive monitoring for glucose levels 9 T1DM patients for 5 days Data-driven 30 min prediction horizon [270]
autoregressive model
4 CGM with meal information, Accurate glucose forecasting 6 T1DM patients for 8 weeks GluNet (CNN) 19.2 mg/dL RMSE and 11.3 min time lag for 30 [271]
insulin doses min prediction horizon
5 CGM, insulin, meal and physical Continuous glucose monitoring using Dataset collected from 112 participants (35 RNN Achieved a blood glucose inference accuracy of [272]
activity smartphones healthy, 38 with T1DM, and 39 with 82.14%
T2DM)
6 Blood glucose, insulin doses, meal To make either insulin or carbohydrate 12 subjects with T1DM from OhioT1DM 2 LSTM chain 8.99 mg/dL RMSE for the carbohydrate [273]
time and carbohydrate estimates recommendations dataset recommendation
7 Glucose level, insulin bolus, and For forecasting glucose levels Dataset of 10 simulated cases and 10 Modified RNN with RMSE of 9.38 and 18.87 mg/dL in simulated [274]
meal clinical cases LSTM and clinical cases, respectively
8 CGM and exogenous events Insulin bolus advisor 10 adult subjects and 10 adolescent Deep reinforcement Average percentage time of 80.9% and 61.6% [275]
subjects from UVA/Padova T1D simulator learning in the adult and adolescent cohorts,
respectively
9 3 CGM (Abbott Diabetes, To predict the future glucose level of a new Heterogeneous population of 451 T1DM LSTM Good prediction accuracy for both short-term [276]
DexCom, Medtronic) patient patients (5.93 mg/dL RMSE, 30 min) and long-term
(13.21 mg/dL RMSE, 60 min) prediction
10 Blood glucose Accurate prediction of blood glucose 40 T2DM patients Transfer learning Over 95% prediction accuracy and 90% [277]
variations in T2DM sensitivity for
1 h prediction horizon
11 Glucose, insulin and carbohydrate Glucose predictor and patient classifier 16 T1DM and 6 T2DM patients CNN-based adversarial 19.92 mg/dL RMSE and 8.50 mg/dL MAPE [278]
transfer learning
12 Sweat glucose For measuring glucose concentrations from 3 human subjects DT RMSE of 0.1mg/dL [279]
sweat
13 CGM, HR, steps, sleep and To forecast the occurrence of hypoglycemia 10 T1DM patients SVM and MLP SVM achieved the best results in predicting [280]
calories in the period when patients were sleeping nocturnal hypoglycemia
CGM: Continuous glucose monitoring; T1DM: type 1 diabetes mellitus; ARIMA: autoregressive integrated moving average; RF: random forest; SVM: support vector machines; RMSE: root-mean-square error; KNN: k
nearest neighbors; LSTM: long short-term memory; T1D: type 1 diabetes; T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus; MAPE: mean percentage absolute error; DT: decision tree; HR: heart rate; MLP: multilayer perceptron
networks.
computation and pattern recognition occur, and an output layer that delivers the prediction or classification. The principle behind ANNs involves the neurons
in each layer processing the input data and applying weights that are adjusted during training to minimize error in the output. This process, known as