Page 78 - Read Online
P. 78
Lin et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:14 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.05 Page 15 of 25
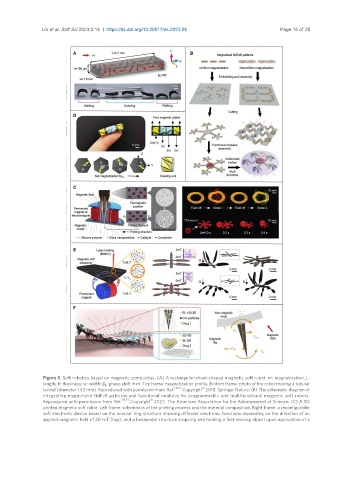
Figure 5. Soft robotics based on magnetic composites. (A) A rectangular-sheet-shaped magnetic soft robot. m: magnetization; L:
length; h: thickness; w: width; β : phase shift in m. Top frame: magnetization profile. Bottom frame: photo of the robot moving a tubular
R
©
tunnel (diameter 1.62 mm). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [153] . Copyright 2018. Springer Nature; (B) The schematic diagram of
integrating magnetized NdFeB patterns and functional modules for programmable and multifunctional magnetic soft robots.
©
Reproduced with permission from Ref. [154] . Copyright 2022. The American Association for the Advancement of Science; (C) A 3D
printed magnetic soft robot. Left frame: schematics of the printing process and the material composition. Right frame: a reconfigurable
soft electronic device based on the annular ring structure showing different electronic functions depending on the direction of an
applied magnetic field of 30 mT (top); and a hexapedal structure stopping and holding a fast-moving object upon application of a