Page 166 - Read Online
P. 166
Tu et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:25 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.15 Page 5 of 15
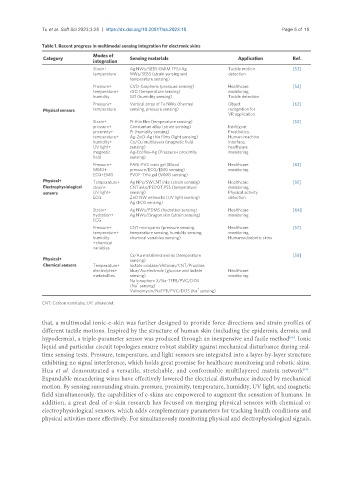
Table 1. Recent progress in multimodal sensing integration for electronic skins
Modes of
Category Sensing materials Application Ref.
integration
Strain+ Ag NWs/SEBS-EMIM TFSI-Ag Tactile motion [53]
temperature NWs/SEBS (strain sensing and detection
temperature sensing)
Pressure+ CVD-Graphene (pressure sensing) Healthcare [54]
temperature+ rGO (temperature sensing) monitoring,
humidity GO (humidity sensing) Tactile detection
Pressure+ Vertical array of Te NWs (thermal Object [62]
Physical sensors temperature sensing, pressure sensing) recognition for
VR application
Strain+ Pt thin film (temperature sensing) [52]
pressure+ Constantan alloy (strain sensing) Intelligent
proximity+ PI (humidity sensing) Prosthetics,
temperature+ Ag-ZnO-Ag thin films (light sensing) Human-machine
humidity+ Co/Cu multilayers (magnetic field interface,
UV light+ sensing) healthcare
magnetic Ag-Ecoflex-Ag (Pressure+ proximity monitoring
field sensing)
Pressure+ PANi-PVC ionic gel (Blood Healthcare [63]
MMG+ pressure/ECG/EMG sensing) monitoring
ECG+EMG PVDF-TrFe gel (MMG sensing)
Physical+ Temperature+ Ag NPs/SWCNT inks (strain sensing) Healthcare [55]
Electrophysiological strain+ CNT inks/PEDOT:PSS (temperature monitoring,
sensors UV light+ sensing) Physical activity
ECG ZnO NW networks (UV light sensing) detection
Ag (ECG sensing)
Strain+ Ag NWs/PDMS (hydration sensing) Healthcare [64]
hydration+ Ag NWs/Dragon skin (strain sensing) monitoring
ECG
Pressure+ CNT microyarns (pressure sensing, Healthcare [57]
temperature+ temperature sensing, humidity sensing, monitoring,
humidity chemical variables sensing) Humanoid robotic skins
+chemical
variables
Cr/Au metal microwires (temperature [58]
Physical+ sensing)
Chemical sensors Temperature+ lactate oxidase/chitosan/CNT/Prussian
electrolytes+ blue/Au electrode (glucose and lactate Healthcare
metabolites sensing) monitoring
Na ionophore X/Na-TFPB/PVC/DOS
+
(Na sensing)
+
Valinomycin/NaTPB/PVC/DOS (Ka sensing)
CNT: Carbon nanotube; UV: ultraviolet.
that, a multimodal ionic-e-skin was further designed to provide force directions and strain profiles of
different tactile motions. Inspired by the structure of human skin (including the epidermis, dermis, and
hypodermis), a triple-parameter sensor was produced through an inexpensive and facile method . Ionic
[66]
liquid and particular circuit topologies ensure robust stability against mechanical disturbance during real-
time sensing tests. Pressure, temperature, and light sensors are integrated into a layer-by-layer structure
exhibiting no signal interference, which holds great promise for healthcare monitoring and robotic skins.
Hua et al. demonstrated a versatile, stretchable, and conformable multilayered matrix network .
[52]
Expandable meandering wires have effectively lowered the electrical disturbance induced by mechanical
motion. By sensing surrounding strain, pressure, proximity, temperature, humidity, UV light, and magnetic
field simultaneously, the capabilities of e-skins are empowered to augment the sensation of humans. In
addition, a great deal of e-skin research has focused on merging physical sensors with chemical or
electrophysiological sensors, which adds complementary parameters for tracking health conditions and
physical activities more effectively. For simultaneously monitoring physical and electrophysiological signals,