Page 52 - Read Online
P. 52
Pintos-Morell et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2024;3:12 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2023.52 Page 11 of 15
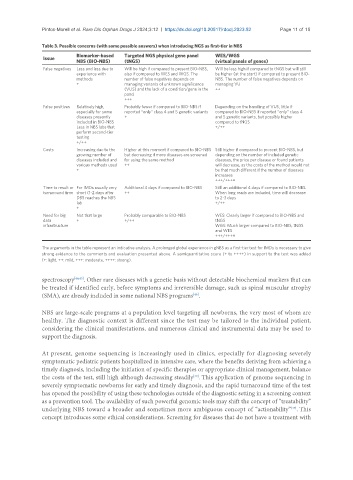
Table 3. Possible concerns (with some possible answers) when introducing NGS as first-tier in NBS
Biomarker-based Targeted NGS physical gene panel WES/WGS
Issue
NBS (BIO-NBS) (tNGS) (virtual panels of genes)
False negatives Less and less due to Will be high if compared to present BIO-NBS, Will be less high if compared to tNGS but will still
experience with also if compared to WES and WGS. The be higher (at the start) if compared to present BIO-
methods number of false negatives depends on NBS. The number of false negatives depends on
+ managing variants of unknown significance managing VU
(VUS) and the lack of a condition/gene in the ++
panel
+++
False positives Relatively high, Probably fewer if compared to BIO-NBS if Depending on the handling of VUS, little if
especially for some reported “only” class 4 and 5 genetic variants compared to BIO-NBS if reported “only” class 4
diseases presently + and 5 genetic variants, but possibly higher
included in BIO-NBS compared to tNGS
Less in NBS labs that +/++
perform second-tier
testing
+/++
Costs Increasing due to the Higher at this moment if compared to BIO-NBS Still higher if compared to present BIO-NBS, but
growing number of but decreasing if more diseases are screened depending on the number of included genetic
diseases included and for using the same method diseases, the price per disease or found patients
various methods used ++ will decrease, as the costs of the method would not
+ be that much different if the number of diseases
increases
+++/++++
Time to result or For IMDs usually very Additional 4 days if compared to BIO-NBS Still an additional 4 days if compared to BIO-NBS.
turnaround time short (1-2 days after ++ When long reads are included, time will decrease
DBS reaches the NBS to 2-3 days
lab +/++
+
Need for big Not that large Probably comparable to BIO-NBS WES: Clearly larger if compared to BIO-NBS and
data + +/++ tNGS
infrastructure WGS: Much larger compared to BIO-NBS, tNGS
and WES
+++/++++
The arguments in the table represent an indicative analysis. A prolonged global experience in gNBS as a first-tier test for IMDs is necessary to give
strong evidence to the comments and evaluation presented above. A semiquantitative score (+ to ++++) in support to the text was added
(+: light, ++: mild, +++: moderate, ++++: strong).
spectroscopy [44,45] . Other rare diseases with a genetic basis without detectable biochemical markers that can
be treated if identified early, before symptoms and irreversible damage, such as spinal muscular atrophy
(SMA), are already included in some national NBS programs .
[46]
NBS are large-scale programs at a population level targeting all newborns, the very most of whom are
healthy. The diagnostic context is different since the test may be tailored to the individual patient,
considering the clinical manifestations, and numerous clinical and instrumental data may be used to
support the diagnosis.
At present, genome sequencing is increasingly used in clinics, especially for diagnosing severely
symptomatic pediatric patients hospitalized in intensive care, where the benefits deriving from achieving a
timely diagnosis, including the initiation of specific therapies or appropriate clinical management, balance
[29]
the costs of the test, still high although decreasing steadily . This application of genome sequencing in
severely symptomatic newborns for early and timely diagnosis, and the rapid turnaround time of the test
has opened the possibility of using these technologies outside of the diagnostic setting in a screening context
as a prevention tool. The availability of such powerful genomic tools may shift the concept of “treatability”
underlying NBS toward a broader and sometimes more ambiguous concept of “actionability” . This
[47]
concept introduces some ethical considerations. Screening for diseases that do not have a treatment with