Page 49 - Read Online
P. 49
Page 8 of 15 Pintos-Morell et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2024;3:12 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2023.52
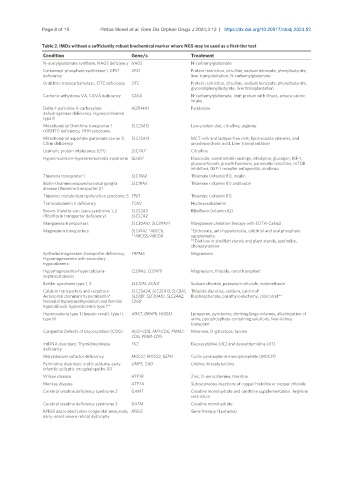
Table 2. IMDs without a sufficiently robust biochemical marker where NGS may be used as a first-tier test
Condition Gene/s Treatment
N-acetylglutamate synthase, NAGS deficiency NAGS N-carbamylglutamate
Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I, CPS1 CPS1 Protein restriction, citrulline, sodium benzoate, phenylbutyrate,
deficiency liver transplantation, N-carbamylglutamate
Ornithine transcarbamylase, OTC deficiency OTC Protein restriction, citrulline, sodium benzoate, phenylbutyrate,
glycerol phenylbutyrate, liver transplantation
Carbonic anhydrase VA, CAVA deficiency CA5A N-carbamylglutamate, limit protein with illness, ensure caloric
intake
Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate ALDH4A1 Pyridoxine
dehydrogenase deficiency, Hyperprolinemia
type II
Mitochondrial Ornithine transporter 1 SLC25A15 Low-protein diet, citrulline, arginine
(ORNT1) deficiency, HHH syndrome
Mitochondrial aspartate glutamate carrier 2, SLC25A13 MCT milk and lactose-free milk, lipid-soluble vitamins, and
Citrin deficiency ursodeoxycholic acid. Liver transplantation
Lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI) SLC7A7 Citrulline
Hyperinsulinism-hyperammonemia syndrome GLUD1 Diazoxide, somatostatin analogs, nifedipine, glucagon, IGF-1,
glucocorticoids, growth hormone, pancreatic resection, mTOR
inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor antagonists, sirolimus
Thiamine transporter 1 SLC19A2 Thiamine (vitamin B1), insulin
Biotin-thiamine responsive basal ganglia SLC19A3 Thiamine (vitamin B1) and biotin
disease (thiamine transporter 2)
Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 5 TPK1 Thiamine (vitamin B1)
Transcobalamin II deficiency TCN2 Hydroxocobalamin
Brown-Vialetto-van Laere syndrome 1, 2 SLC52A3 Riboflavin (vitamin B2)
(Riboflavin transporter deficiency) SLC52A2
Manganese transporters SLC30A10, SLC39A14 Manganese chelation therapy with EDTA-CaNa2
Magnesium transporters SLC41A1, *ABCC6, *Etidronate, anti-hypertensive, calcitriol and oral phosphate
**ABCG5/ABCG8 supplements
**Diet low in shellfish sterols and plant sterols, ezetimibe,
cholestyramine
Epithelial magnesium transporter deficiency, TRPM6 Magnesium
Hypomagnesemia with secondary
hypocalcemia
Hypomagnesemia-hypercalciuria- CLDN16, CLDN19 Magnesium, thiazide, renal transplant
nephrocalcinosis
Bartter syndrome type 1, 2 SLC12A1, KCNJ1 Sodium chloride, potassium chloride, indomethacin
Calcium transporters and receptors: SLC25A24, SLC25A13, SLC8A1, Thiazide diuretics, calcium, calcitriol*
Autosomal dominant hypocalcemia* SLC8B1, SLC30A10, SLC24A2, Bisphosphonate, parathyroidectomy, cinacalcet**
Neonatal hyperparathyroidism and familial CASR
hypocalciuric hypercalcemia type I**
Hyperoxaluria type 1 (hepato-renal), type II, AGXT, GRHPR, HOGA1 Lumasiran, pyridoxine, drinking large volumes, alkalinization of
type III urine, pyrophosphate-containing solutions, liver-kidney
transplant
Congenital Defects of Glycosylation (CDG) ALG1-CDG, MPI-CDG, PMM2- Mannose, D-galactose, fucose
CDG, PGM1-CDG
mtDNA disorders: Thymidine kinase TK2 Deoxycytidine (dC) and deoxythymidine (dT)
deficiency
Molybdenum cofactor deficiency MOCS1, MOCS2, GEPH Cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate (MOCS1)
Pyrimidine disorders: orotic aciduria, early UMPS, CAD Uridine, triacetyluridine
infantile epileptic encephalopathy-50
Wilson disease ATP7B Zinc, D-penicillamine, trientine
Menkes disease ATP7A Subcutaneous injections of copper histidine or copper chloride
Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 2 GAMT Creatine monohydrate and ornithine supplementation. Arginine
restriction
Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 3 GATM Creatine monohydrate
RPE65 associated Leber congenital amaurosis, RPE65 Gene therapy (Luxturna)
early-onset severe retinal dystrophy