Page 831 - Read Online
P. 831
Mirastschijski et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:70 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.147 Page 7 of 14
Table 2. Hormonal differences between genital and non-genital skin of both sexes
Genital skin Non-genital skin
Androgen receptor Higher expression in labia majora and minora; Only present in hair follicles and pilo-sebaceous duct
Upregulated in fibroblasts and basal keratinocytes; keratinocytes;
Co-localization with ER Low expression in extra-genital skin
Oestrogen receptors Highly expressed in penis and labia minora; Lower expression compared to vulva or vagina;
Restricted to basal keratinocytes and stromal fibroblasts; Expressed by keratinocytes and fibroblasts;
Expression decreases with age Absence in skin appendages or blood vessels
Testosterone AR binding capacity of Testosterone higher; Higher rate of conversion testosterone into DHT;
30 times faster degradation; Higher 5-α-reductase activity with irreversible
Reduced effect on aromatase activity in low oxygen formation of DHT
conditions
Oestrogens No conversion of 17β-estradiol into the weaker estrone; 3-fold increased metabolism of 17β-estradiol into the
Stimulate fibroblast contractility without ASMA weaker estrone
expression
Aromatase Higher activity in fibroblasts with conversion of Expression in skin fibroblasts, keratinocytes of the
testosterone into 17β-estradiol; outer root sheath and in terminal hair follicles and in
Dose-dependent reduced activity by testosterone; cells of sebaceous glands and ducts
Aromatase expression is androgen dependent
AR: androgen receptor; ER: oestrogen receptors; DHT: dihydrotestosterone; ASMA: alpha smooth muscle actin
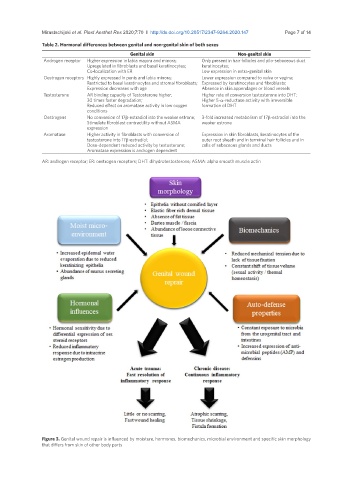
Figure 3. Genital wound repair is influenced by moisture, hormones, biomechanics, microbial environment and specific skin morphology
that differs from skin of other body parts