Page 521 - Read Online
P. 521
Corthouts et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:46 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.97 Page 7 of 15
Palate repair inhibits the forward displacement of the basal maxilla patients with complete UCLP There were considerable similar affected by the different surgical protocols so far. A final evaluation the facial skeleton is complete increases the need for Le Fort 1 osteotomies groups 1,2 and 3. This indicates that the technique of hard palate
Conclusion Significant craniofacial morphological craniofacial growth and development
displacement of the basal maxilla and anteroposterior development of the maxillary dentoalveolus but has no detrimental effects on the downward Lip repair is a most important factor in the restraint of maxillary growth in sagittal growth of the facial skeleton in both centers which has not been should be delayed until the growth of ESGAP seems to have an inhibiting influence on maxillary growth which differences were identifi
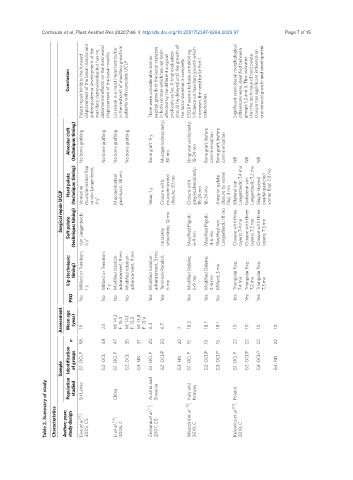
Alveolar cleft (technique; timing) Mucoperiosteoplasty;
No bone grafting No bone grafting No bone grafting No bone grafting Bone graft: 9 y 30 mo Gingivoalveoloplasty; 18-24 mo Bone graft; before canine eruption Bone graft; before canine eruption NR NR NR
Hard palate mucoperiosteal flap
(technique; timing) Vomerine or von Langenbeck; Mucoperiosteal pushback; 38 mo Veau; 1 y Closure with mucoperiosteal closure; 30 mo Closure with gingivoalveoplasty; 18-24 mo 18-24 mo Anterior palate closure by vomer flap; 3 mo Bilateral von Langenbeck; 7.4 mo Unilateral von Langenbeck; 7.2 mo Single-layered caudal-pedicled vomer flap; 7.3 mo
Surgical repair UCLP 4 y a
Soft palate (technique; timing) von Langenbeck; 5 y a Intravelar veloplasty; 12 mo Modified Pigott; 6-9 mo Modified Pigott; 4-6 mo Modified von Langenbeck; 18 mo Closure with three layers; 7.4 mo Closure with three layers; 7.2 mo Closure with three layers; 7.3 mo
Lip (technique;
timing) Millard or Tennison; Millard or Tennison; Modified rotation- advancement; 9 mo Modified rotation- advancement; 9 mo Modified rotation- advancement; 3 mo Tennison-Randall; 6 mo Modified Delaire; 6-9 mo Modified Delaire; 4-6 mo Millard; 3 mo Triangular flap; 7.4 mo Triangular flap; 7.2 mo Triangular flap; 7.3 mo
PSO No 1 y No 7 y No No Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes
Assessment Mean age (year)
19 23 M: 14.2 F: 15.3 M: 14.1 F: 13.3 M: 13.8 F: 13.9 6.3 6.7 7 18.2 18.7 18.1 10 10 10 10
n
58 48 47 35 37 20 20 20 15 10 15 22 22 22 22
Identification of groups G1: OCLP G2: OCL G1: OCLP G2: OCL G3: NN G1: OCLP G2: OCLP G3: NN G1: OCLP G2: OCLP G3: OCLP G1: OCLP G2: OCLP G3: OCLP G4: NN
Sample Austria and
Table 2. Summary of study Characteristics Author; year; Population study design studied Sri Lanka Liao et al. [9] ; 2005; CS China Li et al. [10] ; 2006; C Zemann et al. [11] ; Slovenia 2007; CS Italy and Meazzini et al. [12] ; Norway 2010; C Poland Kulewicz et al. [13] ; 2010; C