Page 110 - Read Online
P. 110
Bradley et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2019;6:11 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2019.06 Page 7 of 13
Table 1. Distribution of operative cases of ZMC fractures in 2016: including ORIF ZMC only,
ORIF ZMC and associated operative procedures, and indirect reduction (Gillies and Keen’s)
OPERATION Number (n), (%)
ORIF Total = 39
ORIF ZMC only 27 (69%)
ORIF ZMC + Orbital floor exploration 4 (10%)
ORIF ZMC + Orbital floor repair 3 (7.5%)
ORIF ZMC + ORIF Le Fort 2 (5%)
ORIF ZMC + ORIF Mandible + ORIF Le Fort 2 (5%)
ORIF ZMC + Nasal MUA 1 (2.5%)
BONE GRAFT Total = 1
Not possible to reduce fracture intra-operatively 1
INDIRECT REDUCTION Total = 13
Gillies lift 11 (85%)
Keen’s 2 (15%)
ORIF: Open Reduction and Internal Fixation; ZMC: zygomatic complex
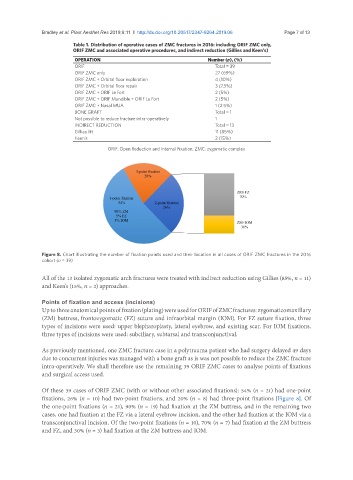
Figure 8. Chart illustrating the number of fixation points used and their location in all cases of ORIF ZMC fractures in the 2016
cohort (n = 39)
All of the 13 isolated zygomatic arch fractures were treated with indirect reduction using Gillies (85%, n = 11)
and Keen's (15%, n = 2) approaches.
Points of fixation and access (incisions)
Up to three anatomical points of fixation (plating) were used for ORIF of ZMC fractures: zygomaticomaxillary
(ZM) buttress, frontozygomatic (FZ) suture and infraorbital margin (IOM). For FZ suture fixation, three
types of incisions were used: upper blepharoplasty, lateral eyebrow, and existing scar. For IOM fixations,
three types of incisions were used: subciliary, subtarsal and transconjunctival.
As previously mentioned, one ZMC fracture case in a polytrauma patient who had surgery delayed 49 days
due to concurrent injuries was managed with a bone graft as is was not possible to reduce the ZMC fracture
intra-operatively. We shall therefore use the remaining 39 ORIF ZMC cases to analyse points of fixations
and surgical access used.
Of these 39 cases of ORIF ZMC (with or without other associated fixations): 54% (n = 21) had one-point
fixations, 26% (n = 10) had two-point fixations, and 20% (n = 8) had three-point fixations [Figure 8]. Of
the one-point fixations (n = 21), 90% (n = 19) had fixation at the ZM buttress, and in the remaining two
cases, one had fixation at the FZ via a lateral eyebrow incision, and the other had fixation at the IOM via a
transconjunctival incision. Of the two-point fixations (n = 10), 70% (n = 7) had fixation at the ZM buttress
and FZ, and 30% (n = 3) had fixation at the ZM buttress and IOM.