Page 106 - Read Online
P. 106
Bradley et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2019;6:11 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2019.06 Page 3 of 13
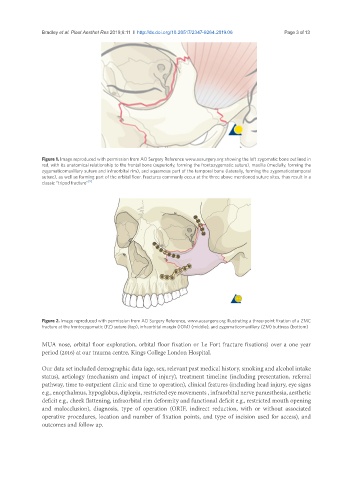
Figure 1. Image reproduced with permission from AO Surgery Reference www.aosurgery.org showing the left zygomatic bone outlined in
red, with its anatomical relationship to the frontal bone (superiorly, forming the frontozygomatic suture), maxilla (medially, forming the
zygomaticomaxillary suture and infraorbital rim), and squamous part of the temporal bone (laterally, forming the zygomaticotemporal
suture), as well as forming part of the orbital floor. Fractures commonly occur at the three above mentioned suture sites, thus result in a
classic “tripod fracture” [9]
Figure 2. Image reproduced with permission from AO Surgery Reference, www.aosurgery.org illustrating a three-point fixation of a ZMC
fracture at the frontozygomatic (FZ) suture (top), infraorbital margin (IOM) (middle), and zygomaticomaxillary (ZM) buttress (bottom)
MUA nose, orbital floor exploration, orbital floor fixation or Le Fort fracture fixations) over a one year
period (2016) at our trauma centre, Kings College London Hospital.
Our data set included demographic data (age, sex, relevant past medical history, smoking and alcohol intake
status), aetiology (mechanism and impact of injury), treatment timeline (including presentation, referral
pathway, time to outpatient clinic and time to operation), clinical features (including head injury, eye signs
e.g., enopthalmus, hypoglobus, diplopia, restricted eye movements , infraorbital nerve paraesthesia, aesthetic
deficit e.g., cheek flattening, infraorbital rim deformity and functional deficit e.g., restricted mouth opening
and malocclusion), diagnosis, type of operation (ORIF, indirect reduction, with or without associated
operative procedures, location and number of fixation points, and type of incision used for access), and
outcomes and follow up.