Page 34 - Read Online
P. 34
Rampino Cordaro et al. Breast reconstruction, antibiotics and drains
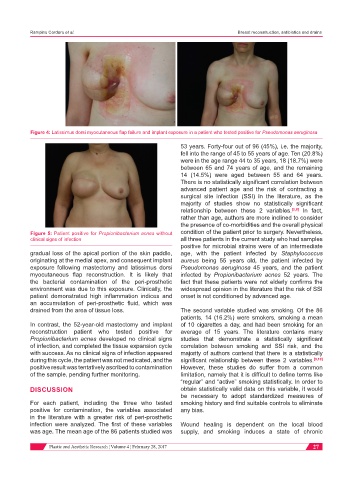
Figure 4: Latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap failure and implant exposure in a patient who tested positive for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
53 years. Forty-four out of 96 (45%), i.e. the majority,
fell into the range of 45 to 55 years of age. Ten (20.8%)
were in the age range 44 to 35 years, 18 (18.7%) were
between 65 and 74 years of age, and the remaining
14 (14.5%) were aged between 55 and 64 years.
There is no statistically significant correlation between
advanced patient age and the risk of contracting a
surgical site infection (SSI) in the literature, as the
majority of studies show no statistically significant
relationship between these 2 variables. [2,8] In fact,
rather than age, authors are more inclined to consider
the presence of co-morbidities and the overall physical
Figure 5: Patient positive for Propionibacterium acnes without condition of the patient prior to surgery. Nevertheless,
clinical signs of infection all three patients in the current study who had samples
positive for microbial strains were of an intermediate
gradual loss of the apical portion of the skin paddle, age, with the patient infected by Staphylococcus
originating at the medial apex, and consequent implant aureus being 55 years old, the patient infected by
exposure following mastectomy and latissimus dorsi Pseudomonas aeruginosa 45 years, and the patient
myocutaneous flap reconstruction. It is likely that infected by Propionibacterium acnes 52 years. The
the bacterial contamination of the peri-prosthetic fact that these patients were not elderly confirms the
environment was due to this exposure. Clinically, the widespread opinion in the literature that the risk of SSI
patient demonstrated high inflammation indices and onset is not conditioned by advanced age.
an accumulation of peri-prosthetic fluid, which was
drained from the area of tissue loss. The second variable studied was smoking. Of the 86
patients, 14 (16.2%) were smokers, smoking a mean
In contrast, the 52-year-old mastectomy and implant of 10 cigarettes a day, and had been smoking for an
reconstruction patient who tested positive for average of 15 years. The literature contains many
Propionibacterium acnes developed no clinical signs studies that demonstrate a statistically significant
of infection, and completed the tissue expansion cycle correlation between smoking and SSI risk, and the
with success. As no clinical signs of infection appeared majority of authors contend that there is a statistically
during this cycle, the patient was not medicated, and the significant relationship between these 2 variables. [9,10]
positive result was tentatively ascribed to contamination However, these studies do suffer from a common
of the sample, pending further monitoring. limitation, namely that it is difficult to define terms like
“regular” and “active” smoking statistically. In order to
DISCUSSION obtain statistically valid data on this variable, it would
be necessary to adopt standardized measures of
For each patient, including the three who tested smoking history and find suitable controls to eliminate
positive for contamination, the variables associated any bias.
in the literature with a greater risk of peri-prosthetic
infection were analyzed. The first of these variables Wound healing is dependent on the local blood
was age. The mean age of the 86 patients studied was supply, and smoking induces a state of chronic
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ February 28, 2017 27