Page 33 - Read Online
P. 33
Rampino Cordaro et al. Breast reconstruction, antibiotics and drains
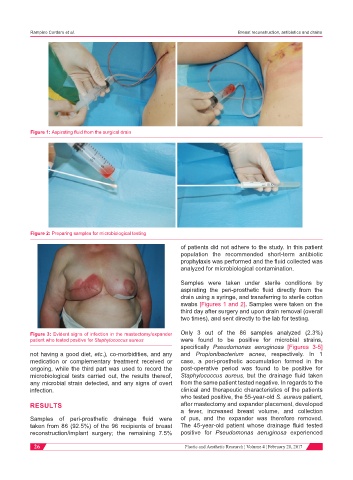
Figure 1: Aspirating fluid from the surgical drain
Figure 2: Preparing samples for microbiological testing
of patients did not adhere to the study. In this patient
population the recommended short-term antibiotic
prophylaxis was performed and the fluid collected was
analyzed for microbiological contamination.
Samples were taken under sterile conditions by
aspirating the peri-prosthetic fluid directly from the
drain using a syringe, and transferring to sterile cotton
swabs [Figures 1 and 2]. Samples were taken on the
third day after surgery and upon drain removal (overall
two times), and sent directly to the lab for testing.
Figure 3: Evident signs of infection in the mastectomy/expander Only 3 out of the 86 samples analyzed (2.3%)
patient who tested positive for Staphylococcus aureus were found to be positive for microbial strains,
specifically Pseudomonas aeruginosa [Figures 3-5]
not having a good diet, etc.), co-morbidities, and any and Propionibacterium acnes, respectively. In 1
medication or complementary treatment received or case, a peri-prosthetic accumulation formed in the
ongoing, while the third part was used to record the post-operative period was found to be positive for
microbiological tests carried out, the results thereof, Staphylococcus aureus, but the drainage fluid taken
any microbial strain detected, and any signs of overt from the same patient tested negative. In regards to the
infection. clinical and therapeutic characteristics of the patients
who tested positive, the 55-year-old S. aureus patient,
RESULTS after mastectomy and expander placement, developed
a fever, increased breast volume, and collection
Samples of peri-prosthetic drainage fluid were of pus, and the expander was therefore removed.
taken from 86 (92.5%) of the 96 recipients of breast The 45-year-old patient whose drainage fluid tested
reconstruction/implant surgery; the remaining 7.5% positive for Pseudomonas aeruginosa experienced
26 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ February 28, 2017