Page 165 - Read Online
P. 165
Omranipour et al. Ipsilateral or contralateral TRAM flap
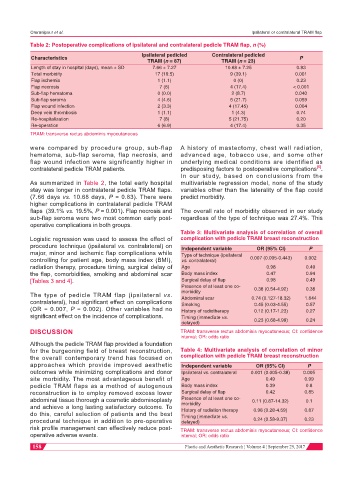
Table 2: Postoperative complications of ipsilateral and contralateral pedicle TRAM flap, n (%)
Ipsilateral pedicled Contralateral pedicled
Characteristics P
TRAM (n = 87) TRAM (n = 23)
Length of stay in hospital (days), mean ± SD 7.66 ± 7.27 10.68 ± 7.25 0.83
Total morbidity 17 (19.5) 9 (39.1) 0.001
Flap ischemia 1 (1.1) 0 (0) 0.23
Flap necrosis 7 (8) 4 (17.4) < 0.001
Sub-flap hematoma 0 (0.0) 2 (8.7) 0.040
Sub-flap seroma 4 (4.6) 5 (21.7) 0.059
Flap wound infection 2 (3.3) 4 (17.45) 0.004
Deep vein thrombosis 1 (1.1) 1 (4.3) 0.74
Re-hospitalization 7 (8) 5 (21.75) 0.20
Re-operation 6 (6.9) 4 (17.4) 0.35
TRAM: transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous
were compared by procedure group, sub-flap A history of mastectomy, chest wall radiation,
hematoma, sub-flap seroma, flap necrosis, and advanced age, tobacco use, and some other
flap wound infection were significantly higher in underlying medical conditions are identified as
contralateral pedicle TRAM patients. predisposing factors to postoperative complications .
[5]
In our study, based on conclusions from the
As summarized in Table 2, the total early hospital multivariable regression model, none of the study
stay was longer in contralateral pedicle TRAM flaps. variables other than the laterality of the flap could
(7.66 days vs. 10.68 days, P = 0.83). There were predict morbidity.
higher complications in contralateral pedicle TRAM
flaps (39.1% vs. 19.5%, P = 0.001). Flap necrosis and The overall rate of morbidity observed in our study
sub-flap seroma were two most common early post- regardless of the type of technique was 27.4%. This
operative complications in both groups.
Table 3: Multivariate analysis of correlation of overall
Logistic regression was used to assess the effect of complication with pedicle TRAM breast reconstruction
procedure technique (ipsilateral vs. contralateral) on Independent variable OR (95% CI) P
major, minor and ischemic flap complications while Type of technique (ipsilateral
controlling for patient age, body mass index (BMI), vs. contralateral) 0.007 (0.005-0.443) 0.002
radiation therapy, procedure timing, surgical delay of Age 0.98 0.49
the flap, comorbidities, smoking and abdominal scar Body mass index 0.47 0.94
[Tables 3 and 4]. Surgical delay of flap 0.98 0.49
Presence of at least one co-
morbidity 0.38 (0.54-4.92) 0.38
The type of pedicle TRAM flap (ipsilateral vs. Abdominal scar 0.74 (0.127-18.32) 1.644
contralateral), had significant effect on complications Smoking 0.45 (0.03-4.55) 0.57
(OR = 0.007, P = 0.002). Other variables had no History of radiotherapy 0.12 (0.17-1.23) 0.27
significant effect on the incidence of complications. Timing (immediate vs.
delayed) 0.23 (0.68-4.99) 0.24
DISCUSSION TRAM: transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous; CI: confidence
interval; OR: odds ratio
Although the pedicle TRAM flap provided a foundation
for the burgeoning field of breast reconstruction, Table 4: Multivariate analysis of correlation of minor
the overall contemporary trend has focused on complication with pedicle TRAM breast reconstruction
approaches which provide improved aesthetic Independent variable OR (95% CI) P
outcomes while minimizing complications and donor Ipsilateral vs. contralateral 0.001 (0.005-0.38) 0.005
site morbidity. The most advantageous benefit of Age 0.49 0.99
pedicle TRAM flaps as a method of autogenous Body mass index 0.39 0.8
reconstruction is to employ removed excess lower Surgical delay of flap 0.42 0.85
abdominal tissue thorough a cosmetic abdominoplasty Presence of at least one co- 0.11 (0.87-14.32) 0.1
and achieve a long lasting satisfactory outcome. To morbidity 0.98 (0.28-4.59) 0.87
History of radiation therapy
do this, careful selection of patients and the best Timing (immediate vs.
procedural technique in addition to pre-operative delayed) 0.24 (0.58-9.37) 0.23
risk profile management can effectively reduce post- TRAM: transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous; CI: confidence
operative adverse events. interval; OR: odds ratio
158 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ September 29, 2017