Page 147 - Read Online
P. 147
Ogundipe et al. Iliac-bone graft reconstruction for benign mandibular pathology
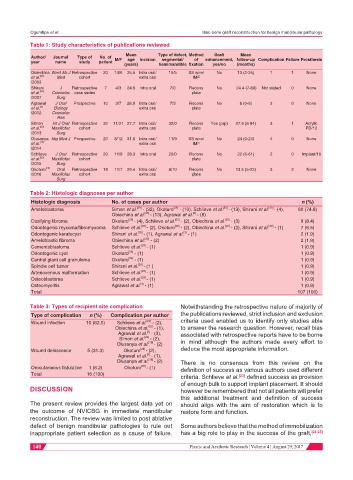
Table 1: Study characteristics of publications reviewed
Mean Type of defect, Method Graft Mean
Author/ Journal Type of No. of M/F age Incision segmental/ of enhancement, follow-up Complication Failure Prosthesis
year name study patient
(years) hemimandible fixation yes/no (months)
Obiechina West Afr J Retrospective 20 14/6 25.5 Intra oral/ 15/5 SS wire/ No 13 (2-25) 1 1 None
et al. [25] Med cohort extra oral IMF
/2003
Shirani J Retrospective 7 4/3 24.6 Intra oral 7/0 Recons No 24.4 (7-60) Not stated 0 None
et al. [30] Craniofac case series plate
/2007 Surg
Agrawal J Oral Prospective 10 3/7 26.9 Intra oral/ 7/3 Recons No 6 (0-6) 3 0 None
et al. [3] Biology extra oral plate
/2012 Craniofac
Res
Simon Int J Oral Retrospective 32 11/21 27.7 Intra oral/ 32/0 Recons Yes (prp) 27.9 (6-84) 3 1 Acrylic
[29]
et al. Maxillofac cohort extra oral plate PD/12
/2013 Surg
Olusanya Nig Med J Prospective 20 8/12 31.6 Intra oral/ 11/9 SS wire/ No 24 (0-24) 4 0 None
et al. extra oral IMF
[19]
/2014
Schlieve J Oral Retrospective 20 11/9 28.3 Intra oral 20/0 Recons No 22 (6-61) 2 0 Implant/10
et al. [23] Maxillofac cohort plate
/2015 Surg
Okoturo [28] Oral Retrospective 18 11/7 29.4 Intra oral/ 8/10 Recons No 13.5 (5-22) 3 2 None
/2016 Maxillofac cohort extra oral plate
Surg
Table 2: Histologic diagnoses per author
Histologic diagnosis No. of cases per author n (%)
[29]
[28]
Ameloblastoma Simon et al. - (32), Okoturo - (10), Schlieve et al. [23] - (13), Shirani et al. [30] - (4), 80 (74.8)
[3]
Obiechina et al. [25] - (13), Agrawal et al. - (8)
[23]
Ossifying fibroma Okoturo [28] - (4), Schlieve et al. - (2), Obiechina et al. - (3) 9 (8.4)
[25]
[25]
[30]
[28]
Odontogenic myxoma/fibromyxoma Schlieve et al. [23] - (2), Okoturo - (2), Obiechina et al. - (2), Shirani et al. - (1) 7 (6.5)
[3]
Odontogenic keratocyst Shirani et al. [30] - (1), Agrawal et al. - (1) 2 (1.9)
[25]
Ameloblastic fibroma Obiechina et al. - (2) 2 (1.9)
Cementoblastoma Schlieve et al. [23] - (1) 1 (0.9)
[28]
Odontogenic cyst Okoturo - (1) 1 (0.9)
Central giant cell granuloma Okoturo - (1) 1 (0.9)
[28]
Spindle cell tumor Shirani et al. [30] - (1 ) 1 (0.9)
Arteriovenous malformation Schlieve et al. [23] - (1) 1 (0.9)
Osteoblastoma Schlieve et al. [23] - (1) 1 (0.9)
[3]
Osteomyelitis Agrawal et al. - (1) 1 (0.9)
Total 107 (100)
Table 3: Types of recipient site complication Notwithstanding the retrospective nature of majority of
Type of complication n (%) Complication per author the publications reviewed, strict inclusion and exclusion
Wound infection 10 (62.5) Schlieve et al. - (2), criteria used enabled us to identify only studies able
[23]
[25]
Obiechina et al. - (1), to answer the research question. However, recall bias
[3]
Agrawal et al. - (3), associated with retrospective reports have to be borne
[29]
Simon et al. - (2),
Olusanya et al. [19] - (2) in mind although the authors made every effort to
Wound dehiscence 5 (31.3) Okoturo [28] - (2), deduce the most appropriate information.
[3]
Agrawal et al. - (1),
Olusanya et al. [19] - (2) There is no consensus from this review on the
Orocutaneous fistulation 1 (6.2) Okoturo [28] - (1) definition of success as various authors used different
Total 16 (100) [23]
criteria. Schlieve et al. defined success as provision
of enough bulk to support implant placement. It should
DISCUSSION however be remembered that not all patients will prefer
this additional treatment and definition of success
The present review provides the largest data yet on should align with the aim of restoration which is to
the outcome of NVICBG in immediate mandibular restore form and function.
reconstruction. The review was limited to post ablative
defect of benign mandibular pathologies to rule out Some authors believe that the method of immobilization
inappropriate patient selection as a cause of failure. has a big role to play in the success of the graft, [23-25]
140 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ August 29, 2017