Page 89 - Read Online
P. 89
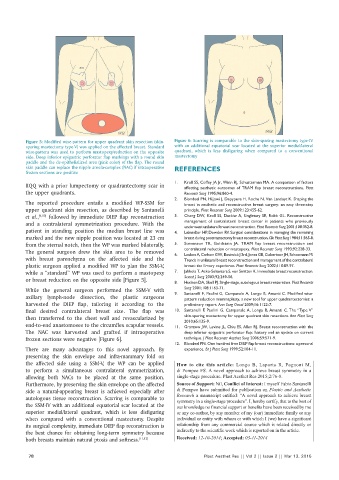
Figure 5: Modified wise‑pattern for upper quadrant skin resection (skin‑ Figure 6: Scarring is comparable to the skin‑sparing mastectomy type‑IV
sparing mastectomy type‑V) was applied on the affected breast. Standard with an additional equatorial scar located at the superior medial/lateral
wise‑pattern was used to perform mastopexy/reduction on the opposite quadrant, which is less disfiguring when compared to a conventional
side. Deep inferior epigastric perforator flap markings with a round skin mastectomy
paddle and the de‑epithelialized area (pink color) of the flap. The round
skin paddle can replace the nipple areola‑complex (NAC) if intraoperative REFERENCES
frozen sections are positive
1. Kroll SS, Coffey JA Jr, Winn RJ, Schusterman MA. A comparison of factors
IIQQ with a prior lumpectomy or quadrantectomy scar in affecting aesthetic outcomes of TRAM flap breast reconstructions. Plast
the upper quadrants. Reconstr Surg 1995;96:860‑4.
2. Blondeel PN, Hijjawi J, Depypere H, Roche N, Van Landuyt K. Shaping the
The reported procedure entails a modified WP‑SSM for breast in aesthetic and reconstructive breast surgery: an easy three‑step
upper quadrant skin resection, as described by Santanelli principle. Plast Reconstr Surg 2009;123:455‑62.
et al., [9,10] followed by immediate DIEP flap reconstruction 3. Chang DW, Kroll SS, Dackiw A, Singletary SE, Robb GL. Reconstructive
and a contralateral symmetrization procedure. With the management of contralateral breast cancer in patients who previously
underwent unilateral breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2001;108:352‑8.
patient in standing position the median breast line was 4. Labandter HP, Dowden RV. Surgical considerations in managing the remaining
marked and the new nipple position was located at 23 cm breast during postmastectomy breast reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 1984;11:365‑8.
from the sternal notch, then the WP was marked bilaterally. 5. Stevenson TR, Goldstein JA. TRAM flap breast reconstruction and
The general surgeon drew the skin area to be removed 6. contralateral reduction or mastopexy. Plast Reconstr Surg 1993;92:228‑33.
Losken A, Carlson GW, Bostwick J 3rd, Jones GE, Culbertson JH, Schoemann M.
with breast parenchyma on the affected side and the Trends in unilateral breast reconstruction and management of the contralateral
plastic surgeon applied a modified WP to plan the SSM‑V, breast: the Emory experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:89‑97.
while a “standard” WP was used to perform a mastopexy 7. Jahkola T, Asko‑Seliavaara S, von Smitten K. Immediate breast reconstruction.
or breast reduction on the opposite side [Figure 5]. Scand J Surg 2003;92:249‑56.
8. Hudson DA, Skoll PJ. Single‑stage, autologous breast restoration. Plast Reconstr
While the general surgeon performed the SSM‑V with Surg 2001;108:1163‑71.
axillary lymph‑node dissection, the plastic surgeons 9. Santanelli F, Paolini G, Campanale A, Longo B, Amanti C. Modified wise‑
pattern reduction mammaplasty, a new tool for upper quadrantectomies: a
harvested the DIEP flap, tailoring it according to the preliminary report. Ann Surg Oncol 2009;16:1122‑7.
final desired contralateral breast size. The flap was 10. Santanelli F, Paolini G, Campanale A, Longo B, Amanti C. The “Type V”
then transferred to the chest wall and revascularized by skin‑sparing mastectomy for upper quadrant skin resections. Ann Plast Surg
2010;65:135‑9.
end‑to‑end anastomoses to the circumflex scapular vessels. 11. Granzow JW, Levine JL, Chiu ES, Allen RJ. Breast reconstruction with the
The NAC was harvested and grafted if intraoperative deep inferior epigastric perforator flap: history and an update on current
frozen sections were negative [Figure 6]. technique. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2006;59:571‑9.
12. Blondeel PN. One hundred free DIEP flap breast reconstructions: a personal
There are many advantages to this novel approach. By experience. Br J Plast Surg 1999;52:104‑11.
preserving the skin envelope and infra‑mammary fold on
the affected side using a SSM‑V, the WP can be applied How to cite this article: Longo B, Laporta R, Pagnoni M,
to perform a simultaneous contralateral symmetrization, di Pompeo FS. A novel approach to achieve breast symmetry in a
allowing both NACs to be placed at the same position. single-stage procedure. Plast Aesthet Res 2015;2:76-8.
Furthermore, by preserving the skin envelope on the affected Source of Support: Nil, Conflict of Interest: I myself Fabio Santanelli
side a natural‑appearing breast is achieved especially after di Pompeo have submitted for publication on Plastic and Aesthetic
autologous tissue reconstruction. Scarring is comparable to Research a manuscript entitled: “A novel approach to achieve breast
symmetry in a single-stage procedure”. I, hereby certify, that to the best of
the SSM‑IV with an additional equatorial scar located at the our knowledge no financial support or benefits have been received by me
superior medial/lateral quadrant, which is less disfiguring or any co-author, by any member of my (our) immediate family or any
when compared with a conventional mastectomy. Despite individual or entity with whom or with which I (we) have a significant
its surgical complexity, immediate DIEP flap reconstruction is relationship from any commercial source which is related directly or
the best chance for obtaining long‑term symmetry because indirectly to the scientific work which is reported on in the article.
both breasts maintain natural ptosis and softness. [11,12] Received: 12-10-2014; Accepted: 03-11-2014
78 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 2 || Mar 13, 2015