Page 85 - Read Online
P. 85
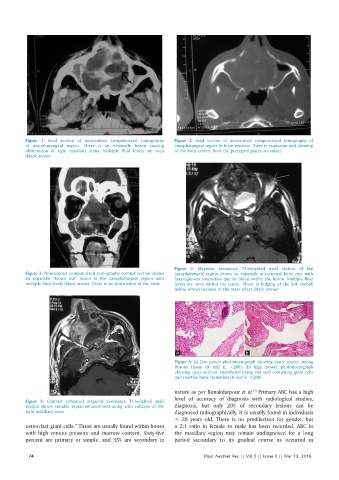
Figure 1: Axial section of noncontrast computerized tomography Figure 2: Axial section of noncontrast computerized tomography of
of nasopharyngeal region. There is an expansile lesion causing nasopharyngeal region in bone window. There is expansion and thinning
obliteration of right maxillary sinus. Multiple fluid levels are seen of the bony cortex. Both the pterygoid plates are intact
(black arrow)
Figure 4: Magnetic resonance T1‑weighted axial section of the
Figure 3: Noncontrast computerized tomography coronal section shows nasopharyngeal region shows an expansile aneurysmal bone cyst with
an expansile “blown out” lesion in the nasopharyngeal region with heterogenous intensities due to blood within the lesion. Multiple fluid
multiple fluid levels (black arrow). There is no destruction of the bone levels are seen within the lesion. There is bulging of the left eyeball
(white arrow) because of the mass effect (black arrow)
a b
Figure 6: (a) Low power photomicrograph showing cystic spaces among
fibrous tissue (H and E, ×200); (b) high power photomicrograph
showing cysts without endothelial lining and wall containing giant cells
and reactive bone formation (H and E, ×200)
nature as per Bonakdarpour et al. Primary ABC has a high
[3]
level of accuracy of diagnosis with radiological studies,
Figure 5: Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance T1‑weighted axial
section shows variable septal enhancement along with collapse of the diagnosis, but only 20% of secondary lesions can be
right maxillary sinus diagnosed radiographically. It is usually found in individuals
< 20 years old. There is no predilection for gender, but
osteoclast giant cells.” These are usually found within bones a 2:1 ratio in female to male has been recorded. ABC in
with high venous pressure and marrow content. Sixty‑five the maxillary region may remain undiagnosed for a long
percent are primary or simple, and 35% are secondary in period secondary to its gradual course as occurred in
74 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 2 || Mar 13, 2015