Page 81 - Read Online
P. 81
RESULTS postoperatively. Regular follow‑up was performed, and
the flap was noted to remain viable [Figure 1f and g].
Six patients presented with malar and lower eyelid defects, Patient with lower eyelid and malar defect
2 patients presented with malar defects, and 1 patient A 36‑year‑old woman sustained an injury resulting in
with upper and lower eyelid and malar defects following
trauma. The patients’ ages ranged from 20 to 36 years soft tissue deficits of the right malar and right lower
(with a mean age of 27 years). Among 9 patients, 7 were eyelid [Figure 2a]. Wound debridement was carried out
males and 2 were females. The defects varied in size with use of the McGregor flap for coverage [Figure 2b].
from 2 cm × 3 cm to 3 cm × 4 cm. A McGregor flap was The patient received three sessions of postoperative
performed in all cases. No secondary procedures were hyperbaric oxygen therapy and the flap healed well
required. Sutures were removed between 7 and 9 days [Figure 2c].
postoperatively. There was no evidence of partial or total Patient with malar defect
flap loss during the follow‑up period [Table 1]. A 21‑year‑old man presented with a defect of the right
Patient with upper and lower eyelid and malar malar region following a road traffic accident [Figure 3a].
defects Wound debridement with McGregor flap coverage was
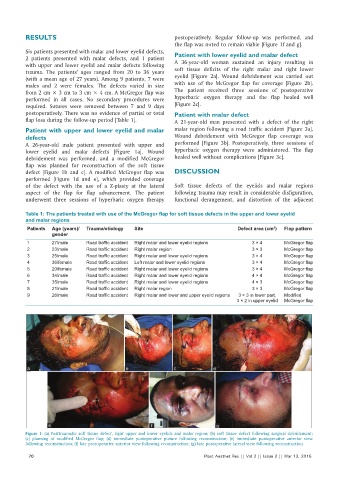
A 26‑year‑old male patient presented with upper and performed [Figure 3b]. Postoperatively, three sessions of
lower eyelid and malar defects [Figure 1a]. Wound hyperbaric oxygen therapy were administered. The flap
debridement was performed, and a modified McGregor healed well without complications [Figure 3c].
flap was planned for reconstruction of the soft tissue
defect [Figure 1b and c]. A modified McGregor flap was DISCUSSION
performed [Figure 1d and e], which provided coverage
of the defect with the use of a Z‑plasty at the lateral Soft tissue defects of the eyelids and malar regions
aspect of the flap for flap advancement. The patient following trauma may result in considerable disfiguration,
underwent three sessions of hyperbaric oxygen therapy functional derangement, and distortion of the adjacent
Table 1: The patients treated with use of the McGregor flap for soft tissue defects in the upper and lower eyelid
and malar regions
Patients Age (years)/ Trauma/etiology Site Defect area (cm ) Flap pattern
2
gender
1 27/male Road traffic accident Right malar and lower eyelid regions 3 × 4 McGregor flap
2 23/male Road traffic accident Right malar region 3 × 3 McGregor flap
3 25/male Road traffic accident Right malar and lower eyelid regions 3 × 4 McGregor flap
4 36/female Road traffic accident Left malar and lower eyelid regions 3 × 4 McGregor flap
5 20/female Road traffic accident Right malar and lower eyelid regions 3 × 4 McGregor flap
6 34/male Road traffic accident Right malar and lower eyelid regions 4 × 4 McGregor flap
7 35/male Road traffic accident Right malar and lower eyelid regions 4 × 3 McGregor flap
8 21/male Road traffic accident Right malar region 3 × 3 McGregor flap
9 26/male Road traffic accident Right malar and lower and upper eyelid regions 3 × 3 in lower part, Modified
3 × 2 in upper eyelid McGregor flap
a b c d
e f g
Figure 1: (a) Posttraumatic soft tissue defect, right upper and lower eyelids and malar region; (b) soft tissue defect following surgical debridement;
(c) planning of modified McGregor flap; (d) immediate postoperative picture following reconstruction; (e) immediate postoperative anterior view
following reconstruction; (f) late postoperative anterior view following reconstruction; (g) late postoperative lateral view following reconstruction
70 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 2 || Mar 13, 2015