Page 75 - Read Online
P. 75
same principles to the recent advance in autologous desired breast volume. A piece of alloderm (approximately
reconstruction the development of the DIEP flap. In 4 cm × 5 cm) is shaped to fit the defect between the
concordance with the TRAM/implant literature, Figus ribs and the lateral edge of the pectoralis window. The
[3]
et al. demonstrated that placement of a sub‑pectoral alloderm is first secured to the rib periostium superiorly
implant and DIEP flap can be safely performed and and inferiorly and is then draped along the lateral
utilized in patients with insufficient abdominal tissue, border of the pectoralis window [Figure 3]. The sizer is
in patients who need correction of breast asymmetries, then exchanged with a smooth, round expander/implant,
and in patients that necessitate augmented volume and and a small pocket along the infero‑lateral breast is
projection because they desire larger breasts. The main dissected for placement of the external port. Saline is
concern with the placement of the expander or implant infused via the external port, and lateral digital pressure
simultaneously with a DIEP flap is potential injury to the
pedicle. The authors describe a series of combined DIEP
flap/expander reconstruction as well as the use of an
alloderm sling to protect the pedicle from any immediate
or delayed injury. The study was approved by review board
of Yale University.
METHODS
Between January 2009 and December 2012, over 250
DIEP flaps were performed, and 91% were bilateral
reconstructions. When clinical assessment demonstrated
inadequate abdominal tissue to reconstruct the patient’s
desired breast size, discussions regarding the simultaneous
use of an expander or implant were undertaken. Patients
with a high probability of postoperative radiation were
not offered the choice of a combined DIEP/expander
procedure. However, history of preoperative radiation Figure 1: Bilateral areola‑sparing mastectomy defects
was not used as exclusion criteria. There were 5
patients who underwent simultaneous DIEP flap and
expander/implant placement. These patient’s charts were
retrospectively reviewed, and data points were collected.
These data points include patient demographics,
co‑morbid conditions, pre‑ or postoperative radiation,
primary disease, operative details, the final volume of
the expander postoperatively, length of follow‑up, and
complications. All patients had postoperative photos
taken 4‑12 months postoperatively. Patients were asked
to assess their satisfaction with the reconstruction using a Figure 2: Standard technique of tissue expander reconstruction:
placement of subpectoral sizer and securing alloderm inferiolaterally
four‑point scale, with the number 1 defined as dissatisfied to the released pectoralis muscle edge. The sizer will be replaced with
and the number 4 as very satisfied. placement of a tissue expander with an external port
Operative technique: alloderm sling
The borders of the breast are outlined preoperatively as is
routinely done in expander‑only reconstruction. Elevation
of DIEP flaps occurs simultaneously while the general
surgeons perform the mastectomy. Perforators are isolated,
and the inferior epigastric pedicles are dissected and
exposed. Once the mastectomies are complete [Figure 1],
the subpectoral dissection is undertaken, and sizers are
placed. Alloderm is routinely used infero‑laterally to
recreate the breast pocket and breast borders. The sizer
is expanded to the desired final size, and the alloderm is
secured in place [Figure 2]. The sizers are then deflated,
and a window is created within the medial portion of the
pectoralis, which allows access to the internal mammary
artery and vein. At this time, dissection of the recipient
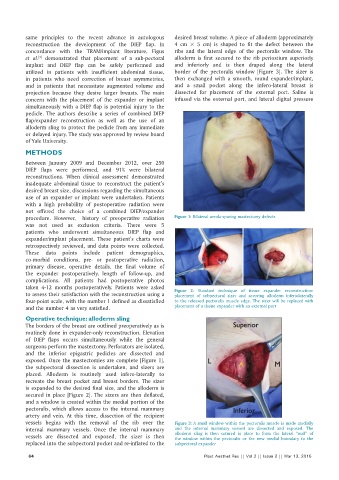
vessels begins with the removal of the rib over the Figure 3: A small window within the pectoralis muscle is made medially
internal mammary vessels. Once the internal mammary and the internal mammary vessesl are dissected and exposed. The
vessels are dissected and exposed, the sizer is then alloderm sling is then sutured in place to form the lateral “wall” of
the window within the pectoralis or the new medial boundary to the
replaced into the subpectoral pocket and re‑inflated to the subpectoral expander
64 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 2 || Mar 13, 2015