Page 15 - Read Online
P. 15
and evaluation of change in garment pressure with and was correlated with sweat volumes measured by
simulated wear and tear, was added to the liposuction gravimetry. Follow‑up after 6 months showed significantly
technique in order to enhance the outcome. improved sweat volumes of 52 ± 41 mg/min of TLC
In 2008, National Institute for Health and Clinical patients versus 78 ± 87 mg/min in the Botox group.
Excellence published guideline on indications and Ninety‑one percent of TLC group and 98% of Botox
patients’ selection for liposuction. group were satisfied with the result. Both methods were
superior to the traditional surgical methods in terms of
Brorson et al. used absence of pitting, failure of efficacy and complication rates. Both Botox and TLC
[27]
conservative treatment, absence of wounds and cancer as improved the quality‑of‑life.
criteria for liposuction for treatment of lymphedema of
upper extremity due to ablative surgery for breast cancer. POSTABLATIVE SURGERY
Literatures review concluded that liposuction
demonstrated significant and stable reduction of both Use of autologous fat grafting for reconstruction is
upper and lower limbs lymphedema. The technique is still controversial because of its safety and efficacy.
also reliable in the treatment of both the acquired and Liposuction is considered an ideal harvesting method for
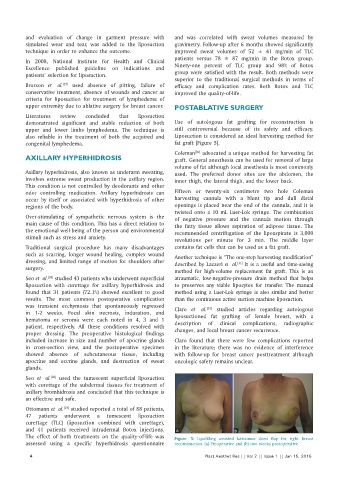
congenital lymphedema. fat graft [Figure 5].
Coleman advocated a unique method for harvesting fat
[30]
AXILLARY HYPERHIDROSIS graft. General anesthesia can be used for removal of large
volume of fat although local anesthesia is most commonly
Axillary hyperhidrosis, also known as underarm sweating, used. The preferred donor sites are the abdomen, the
involves extreme sweat production in the axillary region. inner thigh, the lateral thigh, and the lower back.
This condition is not controlled by deodorants and other
odor controlling medication. Axillary hyperhidrosis can Fifteen or twenty‑six centimetre two hole Coleman
occur by itself or associated with hyperhidrosis of other harvesting cannula with a blunt tip and dull distal
regions of the body. openings is placed near the end of the cannula, and it is
twisted onto a 10 mL Luer‑Lok syringe. The combination
Over‑stimulating of sympathetic nervous system is the of negative pressure and the cannula motion through
main cause of this condition. This has a direct relation to the fatty tissue allows aspiration of adipose tissue. The
the emotional well‑being of the person and environmental recommended centrifugation of the lipoaspirate is 3,000
stimuli such as stress and anxiety.
revolutions per minute for 3 min. The middle layer
Traditional surgical procedure has many disadvantages contains fat cells that can be used as a fat graft.
such as scarring, longer wound healing, complex wound Another technique is “The one‑step harvesting modification”
dressing, and limited range of motion for shoulders after described by Lazzeri et al. It is a useful and time‑saving
[31]
surgery.
method for high‑volume replacement fat graft. This is an
[28]
Seo et al. studied 43 patients who underwent superficial atraumatic, low‑negative‑pressure drain method that helps
liposuction with curettage for axillary hyperhidrosis and to preserves any viable lipocytes for transfer. The manual
found that 31 patients (72.1%) showed excellent to good method using a Luer‑Lok syringe is also similar and better
results. The most common postoperative complication than the continuous active suction machine liposuction.
was transient ecchymosis that spontaneously regressed Claro et al. studied articles regarding autologous
[32]
in 1‑2 weeks. Focal skin necrosis, induration, and liposuctioned fat grafting of female breast, with a
hematoma or seroma were each noted in 4, 3 and 1 description of clinical complications, radiographic
patient, respectively. All these conditions resolved with changes, and local breast cancer recurrence.
proper dressing. The preoperative histological findings
included increase in size and number of apocrine glands Claro found that there were few complications reported
in cross‑section view, and the postoperative specimen in the literature; there was no evidence of interference
showed absence of subcutaneous tissue, including with follow‑up for breast cancer posttreatment although
apocrine and eccrine glands, and destruction of sweat oncologic safety remains unclear.
glands.
[28]
Seo et al. used the tumescent superficial liposuction
with curettage of the subdermal tissues for treatment of
axillary bromhidrosis and concluded that this technique is
an effective and safe.
Ottomann et al. studied reported a total of 88 patients,
[29]
47 patients underwent a tumescent liposuction
curettage (TLC) (liposuction combined with curettage),
and 41 patients received intradermal Botox injections. a b
The effect of both treatments on the quality‑of‑life was Figure 5: Lipofilling assisted latissimus dorsi flap for right breast
assessed using a specific hyperhidrosis questionnaire reconstruction. (a) Preoperative and (b) two weeks postoperative
4 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 1 || Jan 15, 2015