Page 135 - Read Online
P. 135
a b c
d e f
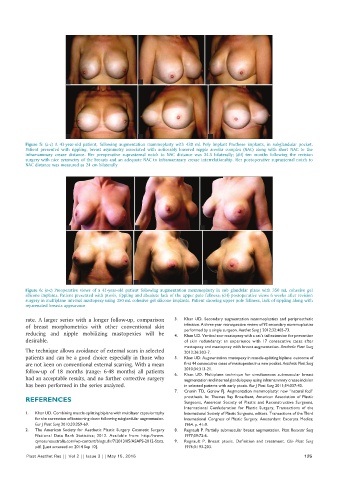
Figure 5: (a-c) A 43-year-old patient, following augmentation mammoplasty with 430 mL Poly Implant Prothese implants, in subglandular pocket.
Patient presented with rippling, breast asymmetry associated with noticeably lowered nipple areolar complex (NAC) along with short NAC to the
inframammary crease distance. Her preoperative suprasternal notch to NAC distance was 24.5 bilaterally; (d-f) ten months following the revision
surgery with nice symmetry of the breasts and an adequate NAC to inframammary crease interrelationship. Her postoperative suprasternal notch to
NAC distance was measured as 24 cm bilaterally
a b c
d e f
Figure 6: (a-c) Preoperative views of a 41-year-old patient following augmentation mammoplasty in sub glandular plane with 350 mL cohesive gel
silicone implants. Patient presented with ptosis, rippling and absolute lack of the upper pole fullness; (d-f) postoperative views 6 weeks after revision
surgery in multiplane internal mastopexy using 350 mL cohesive gel silicone implants. Patient showing upper pole fullness, lack of rippling along with
rejuvenated breasts appearance
rate. A larger series with a longer follow-up, comparison 3. Khan UD. Secondary augmentation mammoplasties and periprosthetic
of breast morphometrics with other conventional skin infection. A three year retrospective review of 92 secondary mammoplasties
reducing and nipple mobilizing mastopexies will be 4. performed by a single surgeon. Aesthet Surg J 2012;32:465‑73.
Khan UD. Vertical scar mastopexy with a cat’s tail extension for prevention
desirable. of skin redundancy: an experience with 17 consecutive cases after
mastopexy and mastopexy with breast augmentation. Aesthetic Plast Surg
The technique allows avoidance of external scars in selected 2012;36:303‑7.
patients and can be a good choice especially in those who 5. Khan UD. Augmentation mastopexy in muscle‑splitting biplane: outcome of
are not keen on conventional external scarring. With a mean first 44 consecutive cases of mastopexies in a new pocket. Aesthetic Plast Surg
follow-up of 18 months (range: 6-48 months) all patients 6. 2010;34:313‑21.
Khan UD. Multiplane technique for simultaneous submuscular breast
had an acceptable results, and no further corrective surgery augmentation and internal glandulopexy using inframammary crease incision
has been performed in the series analyzed. in selected patients with early ptosis. Eur J Plast Surg 2011;34:337‑43.
7. Cronin TD, Gerow FJ. Augmentation mammoplasty: new “natural feel”
REFERENCES prosthesis. In: Thomas Ray Broadbent, American Association of Plastic
Surgeons, American Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons,
International Confederation for Plastic Surgery, Transactions of the
1. Khan UD. Combining muscle‑splitting biplane with multilayer capsulorraphy International Society of Plastic Surgeons, editors. Transactions of the Third
for the correction of bottoming down following subglandular augmentation. International Congress of Plastic Surgery. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica;
Eur J Plast Surg 2010;33:259‑69. 1964. p. 41‑9.
2. The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery Cosmetic Surgery 8. Regnault P. Partially submuscular breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg
National Data Bank Statistics; 2012. Available from: http://www. 1977;59:72‑6.
cynosureaustralia.com/wp‑content/blogs.dir/7/2013/05/ASAPS‑2012‑Stats. 9. Regnault P. Breast ptosis. Definition and treatment. Clin Plast Surg
pdf. [Last accessed on 2014 Sep 10]. 1976;3:193‑203.
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 3 || May 15, 2015 125